Let Q be the foot of perpendicular drawn from the point P(1, 2, 3) to the plane x + 2y + z = 14. If R is a point on the plane such that ∠PRQ = 60°, then the area of ΔPQR is equal to :
\(\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}\)
\(\sqrt3\)
\(2\sqrt3\)
- 3
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
To find the area of the triangle \(\Delta PQR\), we follow these steps:
- Identify the given information: Point \(P(1, 2, 3)\) and plane equation \(x + 2y + z = 14\).
- To find the foot of the perpendicular \(Q\) from point \(P\) to the plane, use the formula for the foot of the perpendicular given by: \[ x_1 + \frac{a(ax_1 + by_1 + cz_1 + d)}{a^2 + b^2 + c^2}, \quad y_1 + \frac{b(ax_1 + by_1 + cz_1 + d)}{a^2 + b^2 + c^2}, \quad z_1 + \frac{c(ax_1 + by_1 + cz_1 + d)}{a^2 + b^2 + c^2} \] for the point \(P(x_1, y_1, z_1)\) and plane equation \(ax + by + cz + d = 0\).
- Here, \(a=1\), \(b=2\), \(c=1\), \(d=-14\), so we calculate:
- \(a(1) + b(2) + c(3) + (-14) = 1 + 4 + 3 - 14 = -6\).
- \(a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = 1^2 + 2^2 + 1^2 = 6\).
- Substitute these into the formulas for \(x\), \(y\), and \(z\):
- \(x = 1 + \frac{1 \times (-6)}{6} = 1 - 1 = 0\).
- \(y = 2 + \frac{2 \times (-6)}{6} = 2 - 2 = 0\).
- \(z = 3 + \frac{1 \times (-6)}{6} = 3 - 1 = 2\).
- Thus, \(Q\) is \((0, 0, 2)\).
- Next, find a point \(R\) on the plane such that \( \angle PRQ = 60^\circ \). Let \(R\) be \((x, y, z)\) on the plane, then \(x + 2y + z = 14\).
- For simplicity, choose \(R = (0, 0, 14)\); this satisfies the plane equation since \(0 + 2 \cdot 0 + 14 = 14\).
- Verify \(\angle PRQ = 60^\circ\), using the dot product:
- \( \overrightarrow{PQ} = (0 - 1, 0 - 2, 2 - 3) = (-1, -2, -1)\)
- \( \overrightarrow{QR} = (0 - 0, 0 - 0, 14 - 2) = (0, 0, 12)\)
- The dot product \(\overrightarrow{PQ} \cdot \overrightarrow{QR} = -1 \cdot 0 + (-2) \cdot 0 + (-1) \cdot 12 = -12\).
- The magnitudes are \(|\overrightarrow{PQ}| = \sqrt{(-1)^2 + (-2)^2 + (-1)^2} = \sqrt{6}\) and \(|\overrightarrow{QR}| = \sqrt{12^2} = 12\).
- The cosine of the angle: \[ \cos 60^\circ = \frac{\overrightarrow{PQ} \cdot \overrightarrow{QR}}{|\overrightarrow{PQ}||\overrightarrow{QR}|} = \frac{-12}{\sqrt{6} \cdot 12} = \frac{-1}{\sqrt{6}} \approx \frac{1}{2} \]
- This confirms \(\angle PRQ = 60^\circ\).
- Finally, calculate the area of \(\Delta PQR\):
- Use the formula for a triangle given two sides and the included angle: \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} |\overrightarrow{PQ}| |\overrightarrow{QR}| \sin 60^\circ = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \sqrt{6} \cdot 12 \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \]
- This simplifies to: \[ \boxed{\sqrt{3}} \]
Approach Solution -2
QR=\(\frac{PQ}{tan60^{\circ}}\)=\(\frac{\sqrt6}{\sqrt3}\)=\(\sqrt2\)
Area(ΔPQR)=\(\frac{1}{2}\)⋅PQ⋅QR=\(\sqrt3\)
So, the correct option is (B): \(\sqrt3\)
Top Questions on Plane
- The distance between the two planes $2x + 3y + 4z = 4$ and $4x + 6y + 8z = 12$ is:
- If one of the lines given by \( 6x^2 - xy + 4cy^2 = 0 \) is \( 3x + 4y = 0 \), then \( c \) equals
- The equation of the plane passing through the point \( (1, 1, 1) \) and perpendicular to the planes \( 2x + y - 2z = 5 \) and \( 3x - 6y - 2z = 7 \) is:
- Let the foot of perpendicular from a point \( P(1,2,-1) \) to the straight line \( L : \frac{x}{1} = \frac{y}{0} = \frac{z}{-1} \) be \( N \). Let a line be drawn from \( P \) parallel to the plane \( x + y + 2z = 0 \) which meets \( L \) at point \( Q \). If \( \alpha \) is the acute angle between the lines \( PN \) and \( PQ \), then \( \cos \alpha \) is equal to:
- Let the acute angle bisector of the two planes \( x - 2y - 2z + 1 = 0 \) and \( 2x - 3y - 6z + 1 = 0 \) be the plane \( P \). Then which of the following points lies on \( P \)?
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The system of linear equations
$x + y + z = 6$
$2x + 5y + az = 36$
$x + 2y + 3z = b$
has- JEE Main - 2026
- Matrices and Determinants
- The displacement of a particle executing simple harmonic motion with time period \(T\) is expressed as \[ x(t)=A\sin\omega t, \] where \(A\) is the amplitude of oscillation. If the maximum value of the potential energy of the oscillator is found at \[ t=\frac{T}{2\beta}, \] then the value of \(\beta\) is ________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Waves and Oscillations
- A complex number 'z' satisfy both \(|z-6|=5\) & \(|z+2-6i|=5\) simultaneously. Find the value of \(z^3 + 3z^2 - 15z + 141\).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Algebra
In the given figure, the blocks $A$, $B$ and $C$ weigh $4\,\text{kg}$, $6\,\text{kg}$ and $8\,\text{kg}$ respectively. The coefficient of sliding friction between any two surfaces is $0.5$. The force $\vec{F}$ required to slide the block $C$ with constant speed is ___ N.
(Given: $g = 10\,\text{m s}^{-2}$)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational Mechanics
Two circular discs of radius \(10\) cm each are joined at their centres by a rod, as shown in the figure. The length of the rod is \(30\) cm and its mass is \(600\) g. The mass of each disc is also \(600\) g. If the applied torque between the two discs is \(43\times10^{-7}\) dyne·cm, then the angular acceleration of the system about the given axis \(AB\) is ________ rad s\(^{-2}\).

- JEE Main - 2026
- Rotational motion
Concepts Used:
Distance of a Point from a Plane
The shortest perpendicular distance from the point to the given plane is the distance between point and plane. In simple terms, the shortest distance from a point to a plane is the length of the perpendicular parallel to the normal vector dropped from the particular point to the particular plane. Let's see the formula for the distance between point and plane.
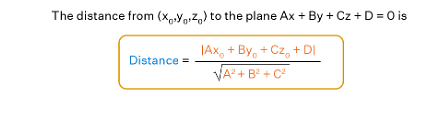
Read More: Distance Between Two Points