If the refractive index from air to glass is $\frac{3}{2}$ and
that from air to water is $\frac{4}{3}$, then the ratio of focal lengths of a glass lens in water and in air is
- $1: 2$
- $2: 1$
- $1: 4$
- $4: 1$
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
To find the ratio of focal lengths of a glass lens when placed in water and in air, we start by understanding the lens maker's formula. The formula for thin lenses is given by:
\(\frac{1}{f} = (n - 1) \left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right)\)
Where:
- \(f\) is the focal length of the lens.
- \(n\) is the refractive index of the material of the lens with respect to the surrounding medium.
- \(R_1\) and \(R_2\) are the radii of curvature of the lens surfaces.
1. **In Air:**
If the lens is in air, the refractive index of glass with respect to air (\(n_{\text{g/a}}\)) is \(\frac{3}{2}\).
The formula becomes:
\(\frac{1}{f_\text{air}} = \left(\frac{3}{2} - 1\right) \left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right) = \frac{1}{2}\left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right)\)
2. **In Water:**
If the lens is in water, first find the refractive index of glass with respect to water (\(n_{\text{g/w}}\)). This can be calculated using relative refractive indices:
\(n_{\text{g/w}} = \frac{n_{\text{g/a}}}{n_{\text{w/a}}} = \frac{\frac{3}{2}}{\frac{4}{3}} = \frac{9}{8}\)
The lens maker's formula for a lens in water becomes:
\(\frac{1}{f_\text{water}} = \left( \frac{9}{8} - 1 \right) \left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right) = \frac{1}{8} \left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right)\)
3. **Finding the Ratio of Focal Lengths:**
Given that the same radii are used, we can compare the two equations:
- \(\frac{1}{f_\text{air}} = \frac{1}{2} \left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right)\)
- \(\frac{1}{f_\text{water}} = \frac{1}{8} \left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right)\)
From these equations, the ratio of focal lengths is calculated as:
\(\frac{f_\text{water}}{f_\text{air}} = \frac{\frac{1}{2}}{\frac{1}{8}} = 4\)
Therefore, the ratio of the focal lengths of a glass lens in water to air is \(4:1\).
The correct answer is: \(4:1\).
Top Questions on Spherical Mirrors
- A concave mirror produces an image of an object such that the distance between the object and image is 20 cm. If the magnification of the image is \( -3 \), then the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- (ii) An object at a distance of 16 cm from a spherical mirror forms a virtual image at a distance of 12 cm behind the mirror. Determine the magnification of the image and type of the mirror.
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- Image of an object formed by a concave mirror is real and of the size of the object. The object is placed -
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- With the help of a suitable ray diagram, derive the formula \( \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f} \) for a concave mirror.
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- The length of the image formed by a concave mirror:
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives
Concepts Used:
Spherical Mirrors
A spherical mirror is a mirror which has been cut out of a spherical surface.
There are two kinds of spherical mirrors:
- Convex Mirror
- Concave Mirror
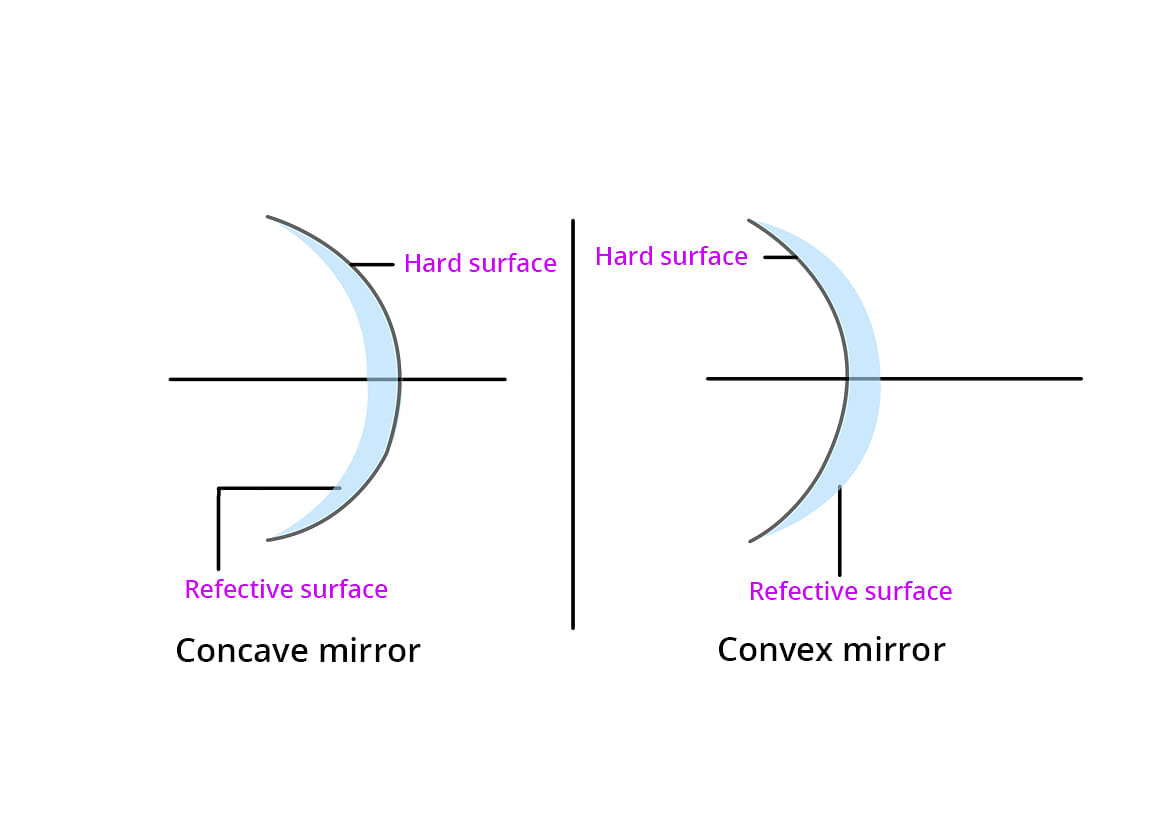
Concave Mirror
Concave mirrors are also called converging mirrors, because in these types of mirrors, light rays converge at a point after impact and reflect back from the reflective surface of the mirror.
Convex Mirror
The convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curved outward. Regardless of the distance between the subject and the mirrors, these mirrors are "always" virtual, upright and reduced.