If A'=\(\begin{bmatrix}-2&3\\1&2\end{bmatrix}\)and B=\(\begin{bmatrix}-1&0\\1&2\end{bmatrix}\),then find (A+2B)'
If A'=\(\begin{bmatrix}-2&3\\1&2\end{bmatrix}\)and B=\(\begin{bmatrix}-1&0\\1&2\end{bmatrix}\),then find (A+2B)'
Solution and Explanation
We know that A=(A')'
so A=\(\begin{bmatrix}-2&1\\3&2\end{bmatrix}\)
so A+2B=\(\begin{bmatrix}-2&1\\3&2\end{bmatrix}\)+2\(\begin{bmatrix}-1&0\\1&2\end{bmatrix}\)
=\(\begin{bmatrix}-2&1\\3&2\end{bmatrix}\)+\(\begin{bmatrix}-2&0\\2&4\end{bmatrix}\)=\(\begin{bmatrix}-4&1\\5&6\end{bmatrix}\)
so (A+2B)'=\(\begin{bmatrix}-4&5\\1&6\end{bmatrix}\)
Top Questions on Matrices
- The number of $3\times2$ matrices $A$, which can be formed using the elements of the set $\{-2,-1,0,1,2\}$ such that the sum of all the diagonal elements of $A^{T}A$ is $5$, is
- If \[ X=\begin{bmatrix}x\\y\\z\end{bmatrix} \] is a solution of the system of equations $AX=B$, where \[ \text{adj }A= \begin{bmatrix} 4 & 2 & 2\\ -5 & 0 & 5\\ 1 & -2 & 3 \end{bmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad B=\begin{bmatrix}4\\0\\2\end{bmatrix}, \] then $|x+y+z|$ is equal to
Let \[ f(x)=\int \frac{7x^{10}+9x^8}{(1+x^2+2x^9)^2}\,dx \] and $f(1)=\frac14$. Given that

- For the matrices \( A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & -4 \\ 1 & -1 \end{bmatrix} \) and \( B = \begin{bmatrix} -29 & 49 \\ -13 & 18 \end{bmatrix} \), if \( (A^{15} + B) \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0\\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \), then among the following which one is true?}
- Let the relation \( R \) on the set \( M = \{1, 2, 3, \ldots, 16\} \) be given by \[ R = \{(x, y) : 4y = 5x - 3,\; x, y \in M\}. \] Then the minimum number of elements required to be added in \( R \), in order to make the relation symmetric, is equal to
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
- A rectangular glass slab ABCD (refractive index 1.5) is surrounded by a transparent liquid (refractive index 1.25) as shown in the figure. A ray of light is incident on face AB at an angle \(i\) such that it is refracted out grazing the face AD. Find the value of angle \(i\).

- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Refraction
- Considering the case of magnetic field produced by air-filled current carrying solenoid, show that the magnetic energy density of a magnetic field \( B \) is \( \frac{B^2}{2\mu_0} \).
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Magnetic Field
- The slope of the curve \( y = -x^3 + 3x^2 + 8x - 20 \) is maximum at:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Maxima and Minima
- Three batteries E1, E2, and E3 of emfs and internal resistances (4 V, 2 \(\Omega\)), (2 V, 4 \(\Omega\)) and (6 V, 2 \(\Omega\)) respectively are connected as shown in the figure. Find the values of the currents passing through batteries E1, E2, and E3.

- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Kirchhoff's Laws
- Two wires made of the same material have the same length \( l \) but different cross-sectional areas \( A_1 \) and \( A_2 \). They are connected together with a cell of voltage \( V \). Find the ratio of the drift velocities of free electrons in the two wires when they are joined in: (i) series, and (ii) parallel.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Current electricity
Concepts Used:
Transpose of a Matrix
The matrix acquired by interchanging the rows and columns of the parent matrix is called the Transpose matrix. The transpose matrix is also defined as - “A Matrix which is formed by transposing all the rows of a given matrix into columns and vice-versa.”
The transpose matrix of A is represented by A’. It can be better understood by the given example:

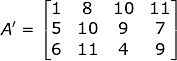
Now, in Matrix A, the number of rows was 4 and the number of columns was 3 but, on taking the transpose of A we acquired A’ having 3 rows and 4 columns. Consequently, the vertical Matrix gets converted into Horizontal Matrix.
Hence, we can say if the matrix before transposing was a vertical matrix, it will be transposed to a horizontal matrix and vice-versa.
Read More: Transpose of a Matrix