Given below are two statements:
Statement I
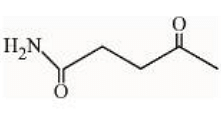
under Clemmensen reduction conditions will give
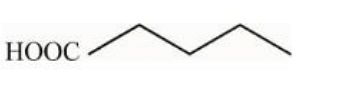
Statement II
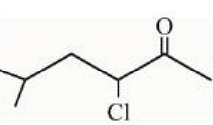
under Wolff-Kishner reduction condition will give
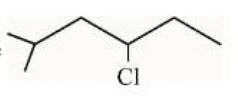
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Given below are two statements:
Statement I

under Clemmensen reduction conditions will give

Statement II

under Wolff-Kishner reduction condition will give

In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Show Hint
Clemmensen Reduction: Reduces ketones or aldehydes to alkanes under acidic conditions.
Wolff-Kishner Reduction: Reduces ketones or aldehydes to alkanes under basic conditions, but reactive substituents like halogens may undergo side reactions.
- Statement I is true but Statement II is false
- Statement I is false but Statement II is true
- Both Statement I and Statement II are true
- Both Statement I and Statement II are false
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Statement I:
Clemmensen reduction involves the use of Zn(Hg) and HCl, which reduces ketones or aldehydes to their corresponding alkanes under acidic conditions.
In the given compound, \(\text{H}_2\text{N} - \text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{COCH}_3\), the ketone group (\(\text{COCH}_3\)) is reduced, and the intermediate carboxylic acid product (\(\text{HOOC-CH}_2\text{CH}_2\)) is correct under these conditions.
Hence, Statement I is true.
Statement II:
Wolff-Kishner reduction involves hydrazine (\(\text{NH}_2\text{NH}_2\)) and a strong base such as KOH, which reduces carbonyl groups (ketones or aldehydes) to their corresponding alkanes.
However, in the compound \(\text{Cl-CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{COCH}_3\), the chlorine atom may react with the basic medium, leading to a side reaction (dehydrohalogenation) instead of simple reduction. The final product will not necessarily be \(\text{ClCH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_3\), as suggested.
Hence, Statement II is false.
Top Questions on Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Iodoform test can differentiate :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
In the given reaction sequence, the structure of Y would be:

- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- The acid formed when propyl magnesium bromide is treated with CO$_2$ followed by acid hydrolysis is:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent, or products: (I) \(\text{CH}_3\text{CH}_3 + \text{KMnO}_4, \text{KOH} \longrightarrow \text{?}\)
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Would you expect benzaldehyde to be more reactive or less reactive in nucleophilic addition reactions than propanal? Justify your answer.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Which of the following best represents the temperature versus heat supplied graph for water, in the range of \(-20^\circ\text{C}\) to \(120^\circ\text{C}\)?

- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
A small block of mass \(m\) slides down from the top of a frictionless inclined surface, while the inclined plane is moving towards left with constant acceleration \(a_0\). The angle between the inclined plane and ground is \(\theta\) and its base length is \(L\). Assuming that initially the small block is at the top of the inclined plane, the time it takes to reach the lowest point of the inclined plane is _______.

- JEE Main - 2026
- General Physics
- A chromium complex with formula CrCl$_3\cdot$6H$_2$O has a spin only magnetic moment value of 3.87 BM and its solution conductivity corresponds to 1:2 electrolyte. 2.75 g of the complex solution was initially passed through a cation exchanger. The solution obtained after the process was reacted with excess of AgNO$_3$. The amount of AgCl formed in the above process is _________ g (Nearest integer).
(Given: Molar mass in g mol$^{-1}$ Cr: 52; Cl: 35.5; Ag:108; O:16; H:1)- JEE Main - 2026
- coordination compounds
- An atom \({}_3^8 X\) is bombarded with electrons, neutrons and protons and in 10 sec, 10 electrons, 10 protons and 9 neutrons are absorbed. If final surface area is x% of initial area, find x : -
- JEE Main - 2026
- Nuclear physics
- Let $\vec{a}=2\hat{i}-\hat{j}-\hat{k}$, $\vec{b}=\hat{i}+3\hat{j}-\hat{k}$ and $\vec{c}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}$. Let $\vec{v}$ be the vector in the plane of $\vec{a}$ and $\vec{b}$, such that the length of its projection on the vector $\vec{c}$ is $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{14}}$. Then $|\vec{v}|$ is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Vector Algebra
Concepts Used:
Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids are carbonyl compounds that contain a carbon-oxygen double bond. These organic compounds are very important in the field of organic chemistry and also have many industrial applications.
Aldehydes:
Aldehydes are organic compounds that have the functional group -CHO.
Preparation of Aldehydes
Acid chlorides are reduced to aldehydes with hydrogen in the presence of palladium catalyst spread on barium sulfate.
Ketones:
Ketones are organic compounds that have the functional group C=O and the structure R-(C=O)-R’.
Preparation of Ketones
Acid chlorides on reaction with dialkyl cadmium produce ketones. Dialkyl cadmium themselves are prepared from Grignard reagents.
Carboxylic Acid:
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a (C=O)OH group attached to an R group (where R refers to the remaining part of the molecule).
Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
Primary alcohols are readily oxidized to carboxylic acids with common oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate in neutral acidic or alkaline media or by potassium dichromate and chromium trioxide in acidic media.