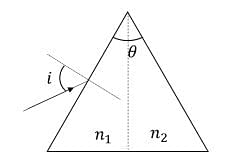
For a prism of prism angle 𝜃 = 60°, the refractive indices of the left half and the right half are, respectively, 𝑛1 and 𝑛2 (𝑛2 ≥ 𝑛1) as shown in the figure. The angle of incidence 𝑖 is chosen such that the incident light rays will have minimum deviation if 𝑛1 = 𝑛2 = 𝑛 = 1.5. For the case of unequal refractive indices, 𝑛1 = 𝑛 and 𝑛2 = 𝑛 +∆𝑛 (where∆𝑛≪𝑛), the angle of emergence \(𝑒 =𝑖+∆𝑒\). Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?

- The value of $\Delta e$ (in radians) is greater than that of $\Delta n$
- $\Delta e$ is proportional to $\Delta n$
- $\Delta e$ lies between $2.0$ and $3.0$ milliradians, if $\Delta n =2.8 \times 10^{-3}$
- $\Delta e$ lies between $1.0$ and $1.6$ milliradians, if $\Delta n =2.8 \times 10^{-3}$
The Correct Option is A, B, C
Solution and Explanation
Step 1: Given Information
We are given the following conditions:
- The prism has an angle of \( \theta = 60^\circ \).
- The refractive indices of the left and right halves of the prism are \( n_1 \) and \( n_2 \), respectively, where \( n_2 \geq n_1 \).
- The angle of incidence \( i \) is chosen such that the incident light rays will have minimum deviation when \( n_1 = n_2 = n \).
- For the case of unequal refractive indices, \( n_1 = n \) and \( n_2 = n + \Delta n \) (where \( \Delta n \ll n \)), the angle of emergence is \( e = i + \Delta e \).
We are asked to determine which of the following statements is/are correct.
Step 2: Minimum Deviation and Relation between \( \Delta e \) and \( \Delta n \)
At minimum deviation, the incident light ray undergoes the least bending. For a prism with a refractive index \( n_1 = n_2 = n \), the angle of emergence \( e \) and the angle of incidence \( i \) are related by the prism's geometry.
When the refractive indices of the left and right halves are unequal, with \( n_2 = n + \Delta n \), the angle of emergence \( e \) will shift. Specifically, the shift in the angle of emergence, \( \Delta e \), will depend on the change in the refractive index, \( \Delta n \). This change is proportional to \( \Delta n \). Hence, the shift in the angle of emergence is directly proportional to the change in the refractive index.
Therefore, statement (B) is correct: \( \Delta e \) is proportional to \( \Delta n \).
Step 3: Estimating \( \Delta e \) for \( \Delta n = 2.8 \times 10^{-3} \)
We are given that \( \Delta n = 2.8 \times 10^{-3} \). We need to estimate the value of \( \Delta e \), which lies between 2.0 and 3.0 milliradians. The value of \( \Delta e \) is small because \( \Delta n \) is small. The linear relationship between \( \Delta e \) and \( \Delta n \) means that if \( \Delta n = 2.8 \times 10^{-3} \), the value of \( \Delta e \) will indeed lie between 2.0 and 3.0 milliradians.
Therefore, statement (C) is correct: \( \Delta e \) lies between 2.0 and 3.0 milliradians if \( \Delta n = 2.8 \times 10^{-3} \).
Final Answer:
The correct options are:
- (B) \( \Delta e \) is proportional to \( \Delta n \)
- (C) \( \Delta e \) lies between 2.0 and 3.0 milliradians if \( \Delta n = 2.8 \times 10^{-3} \)
Top Questions on Ray optics and optical instruments
- Five persons \(P_1, P_2, P_3, P_4\) and \(P_5\) recorded object distance (\(u\)) and image distance (\(v\)) using same convex lens having power \(+5\) D as (25,96), (30,62), (35,37), (45,35) and (50,32) respectively. Identify correct statement.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- In a microscope, the objective has a focal length \(f_o=2\) cm and the eye-piece has a focal length \(f_e=4\) cm. The tube length is 32 cm. The magnification produced by this microscope for normal adjustment is_____.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- In parallax method for the determination of focal length of a concave mirror, the object should always be placed:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- A prism of angle $75^\circ$ and refractive index $\sqrt{3}$ is coated with thin film of refractive index 1.5 only at the back exit surface. To have total internal reflection at the back exit surface the incident angle angle must be ___. ($\sin 15^\circ = 0.25$ and $\sin 25^\circ = 0.43$)}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- Given below are two statements :
Statement I : In a Young's double slit experiment, the angular separation of fringes will increase as the screen is moved away from the plane of the slits
Statement II : In a Young's double slit experiment, the angular separation of fringes will increase when monochromatic source is replaced by another monochromatic source of higher wavelength
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties