Based on the given figure, the number of correct statement/s is/are _______
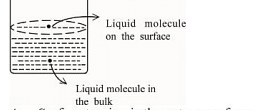
A. Surface tension is the outcome of equal attractive and repulsive forces acting on the liquid molecule in bulk
B. Surface tension is due to uneven forces acting on the molecules present on the surface
C. The molecule in the bulk can never come to the liquid surface
D. The molecules on the surface are responsible for vapour pressure if the system is a closed system

A. Surface tension is the outcome of equal attractive and repulsive forces acting on the liquid molecule in bulk
B. Surface tension is due to uneven forces acting on the molecules present on the surface
C. The molecule in the bulk can never come to the liquid surface
D. The molecules on the surface are responsible for vapour pressure if the system is a closed system
Correct Answer: 2
Solution and Explanation
The correct options are:
B: Surface tension arises due to uneven forces acting on the molecules present at the surface. Molecules at the surface of a liquid experience a net inward force because they are not surrounded by similar molecules on all sides. This imbalance results in the liquid's surface behaving as if it were under tension.
D: The molecules at the surface are responsible for vapor pressure in a closed system. In a closed system, molecules at the surface of the liquid are able to escape into the vapor phase, contributing to the vapor pressure. The equilibrium between the liquid and vapor phases determines the vapor pressure.
Top Questions on States of matter
- Statement-1: Sublimation is a purification technique that is used to separate those solid substances which change from solid to vapor state without passing through liquid state.
Statement-2: If external atmospheric pressure is reduced, then boiling point of substance decreases.
Which of the following is correct?
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Given below are two statements: Statement I: Sublimation is a purification technique that is used to separate those solid substances which change from solid to vapour state without passing through liquid state. Statement II: If external atmospheric pressure is reduced, then boiling point of a substance is decreased. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct option.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- $10^{-6} \text{ M } \text{NaOH}$ is diluted 100 times. The $\text{pH}$ of the diluted base is:
- LPUNEST - 2026
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- $1.0 \times 10^{-4} \text{ M } \text{HCl}$ is diluted 10 times. The $\text{pH}$ of the final solution is:
- LPUNEST - 2026
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- What is the relation between \( \Delta G \) and \( E_{\text{cell}} \)?
- GUJCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- States of matter
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Concepts Used:
States of Matter
The matter is made up of very tiny particles and these particles are so small that we cannot see them with naked eyes.
There are three States of Matter:
The three states of matter are as follows:
Solid State:
- The solid-state is one of the fundamental states of matter.
- Solids differ from liquids and gases by the characteristic of rigidity.
- The molecules of solids are tightly packed because of strong intermolecular forces; they only oscillate about their mean positions.
Liquid State:
- The molecules in a liquid are closely packed due to weak intermolecular forces.
- These forces are weaker than solids but stronger than that of gases.
- There is much space in between the molecules of liquids which makes their flowing ability easy.
Gaseous State:
- In this state of matter, distances between the molecules are large (intermolecular distance is in the range of 10-7-10-5 cm.
- The intermolecular forces experienced between them are negligible.
- Thus, translatory, rotatory and vibratory motions are observed prominently in gases.