A small square loop of wire of side l is placed inside a large square loop of wire L(L>>l). As shown in figure, both loops are coplanar and their centers coincide at point O. The mutual inductance of the system is:
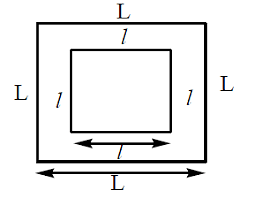

\(\frac{2\sqrt2 \mu_0L^2}{\pi l}\)
\(\frac{\mu_0L^2}{2\sqrt2 \pi L}\)
\(\frac{2\sqrt 2 \mu_0 l^2}{\pi L}\)
\(\frac{\mu_0L^2}{2\sqrt2\pi l}\)
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
B1=4B=\(\frac{4μ_0i}{4π(\frac{L}{2})(2sin45°)}\)
B1=\(\frac{2\sqrt 2 \mu_0 l^2}{\pi L}\)
M=\(\frac{Flux inner loop}{i}\)=\(\frac{2\sqrt 2 \mu_0 il^2}{i\pi ^2}\)
=\(\frac{2\sqrt2 \mu_0l^2}{\pi L}\)
Top Questions on Inductance
- A cylindrical object of density $600\,\text{kg/m}^3$ and height $8$ cm is floating in a liquid of density $900\,\text{kg/m}^3$. Find height of cylinder inside liquid.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Inductance
- If an inductor coil of self-inductance 2H stores 25J of magnetic energy, then the current passing through it is:
- KEAM - 2025
- Physics
- Inductance
- An e.m.f of 5 volts is produced by a self-inductance when the current changes at a steady rate from 3A to 2A in 1 millisecond. The value of self-inductance is:
- MHT CET - 2024
- Physics
- Inductance
- If \( L \) is the inductance and \( R \) is the resistance, then the unit of \( \frac{L}{R} \) is:
- MHT CET - 2024
- Physics
- Inductance
- In a coil, the current changes from \( -2 \, \text{A} \) to \( +2 \, \text{A} \) in \( 0.2 \, \text{s} \) and induces an emf of \( 0.1 \, \text{V} \). The self-inductance of the coil is:
- MHT CET - 2024
- Physics
- Inductance
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- A 20 m long uniform copper wire held horizontally is allowed to fall under the gravity (g = 10 m/s²) through a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.5 Gauss perpendicular to the length of the wire. The induced EMF across the wire when it travels a vertical distance of 200 m is_______ mV.}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- If the end points of chord of parabola \(y^2 = 12x\) are \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) and it subtend \(90^\circ\) at the vertex of parabola then \((x_1x_2 - y_1y_2)\) equals :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Probability
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
Concepts Used:
Inductance
Inductance is a key parameter in electrical and electronic circuit designs. Like resistance and capacitance, it is a basic electrical measurement that affects all circuits to some degree.
Inductance is used in many areas of electrical and electronic systems and circuits. The electronic components can be in a variety of forms and may be called by a variety of names: coils, inductors, chokes, transformers, . . . Each of these may also have a variety of different variants: with and without cores and the core materials may be of different types.
There are two ways in which inductance is used:
- Self-inductance: Self-inductance is the property of a circuit, often a coil, whereby a change in current causes a change in voltage in that circuit due to the magnetic effect of caused by the current flow. It can be seen that self-inductance applies to a single circuit - in other words it is an inductance, typically within a single coil. This effect is used in single coils or chokes.
- Mutual-inductance: Mutual inductance is an inductive effect where a change in current in one circuit causes a change in voltage across a second circuit as a result of a magnetic field that links both circuits. This effect is used in transformers.