A newborn presented with chest retractions, dyspnea, and lethargy. The pediatrician diagnosed the baby with respiratory distress syndrome. This occurs due to the deficiency of:
Dipalmitoyl inositol
- Lecithin
- Sphingomyelin
- Dipalmitoylphosphatidylethanolamine
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) in newborns is primarily caused by a deficiency in surfactant, a substance crucial for reducing surface tension in the alveoli of the lungs. The major component of surfactant is lecithin, also known as phosphatidylcholine.
Lecithin is essential for maintaining alveolar stability and reducing collapse, known as atelectasis, especially in preterm infants who frequently lack sufficient surfactant production due to immature lungs. These factors contribute to the symptoms observed in RDS, such as chest retractions, dyspnea, and lethargy.
Let's review the options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Dipalmitoyl inositol | Not a surfactant component linked with RDS. |
| Lecithin | Primary component of pulmonary surfactant. Deficiency leads to RDS. |
| Sphingomyelin | Not involved in the production of surfactant relevant to RDS. |
| Dipalmitoylphosphatidylethanolamine | Not a primary component of pulmonary surfactant related to RDS. |
Therefore, the deficiency causing respiratory distress syndrome in the newborn is due to insufficient lecithin.
Top Questions on Pediatric Disorders
- A 48-year-old man presents with complaints of facial puffiness, frothy urine, and hypertension. He gives a history of infection with hepatitis B. Urine examination reveals microscopic hematuria. The histopathological image of the kidney biopsy shows a spike and dome pattern. What is the diagnosis of this condition ?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Pathology
- Pediatric Disorders
- A child presented to the hospital with cola-colored urine, hypertension, and puffiness of eyes. Laboratory investigations were done, and creatinine was 2.5 mg/dL. Treatment was started, and despite treatment, the patient did not improve for the next 3 weeks. The creatinine value increased to 4.5 mg/dL. Which among the following electron microscopic findings will be seen in this patient ?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Pathology
- Pediatric Disorders
- A 3-month-old baby presents with jaundice and clay-coloured stools. Lab investigation reveals that the baby has conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. The liver biopsy shows periductal proliferation. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Pediatrics
- Pediatric Disorders
- A child is brought to the hospital with respiratory distress and biphasic stridor. The radiograph is shown below. What is the diagnosis?
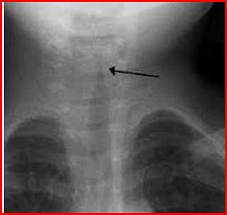
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Pediatrics
- Pediatric Disorders
- An infant is brought with complaints of excessive watering of the eyes and photophobia. The image is given below. What is the likely diagnosis ?

- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Ophthalmology
- Pediatric Disorders
Questions Asked in NEET PG exam
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for the motor innervation of the muscles of mastication?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The normal pH of arterial blood is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
Which enzyme is deficient in Gaucher’s disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is monitored using:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The causative agent of malaria is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science