Question:
A child is brought to the hospital with respiratory distress and biphasic stridor. The radiograph is shown below. What is the diagnosis?
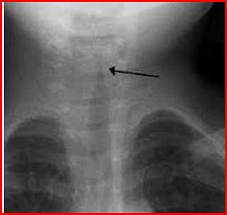
A child is brought to the hospital with respiratory distress and biphasic stridor. The radiograph is shown below. What is the diagnosis?


Updated On: Jun 19, 2025
Acute epiglottitis
- Acute laryngotracheobronchitis
Foreign body aspiration
- Laryngomalacia
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
The child presenting with respiratory distress and biphasic stridor suggests an upper airway obstruction. The radiograph may exhibit characteristic features associated with these symptoms. Here is an analysis of the given options:
- Acute epiglottitis: Typically presents with high fever, drooling, and difficulty swallowing. Radiographs show the classic "thumb sign" due to an enlarged epiglottis.
- Acute laryngotracheobronchitis (Croup): Commonly seen in children, characterized by a barking cough and stridor. Radiographs show the "steeple sign" due to subglottic narrowing.
- Foreign body aspiration: Can cause sudden respiratory distress and localized wheezing. Radiographic findings vary based on the object's location and type.
- Laryngomalacia: Typically affects infants with intermittent stridor, worsening in supine positions. It's a structural condition, usually not seen on x-rays.
The symptoms of respiratory distress and biphasic stridor, coupled with radiographic findings of subglottic narrowing (not visible here but suggested), point towards Acute laryngotracheobronchitis as the diagnosis.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Pediatric Disorders
- A 48-year-old man presents with complaints of facial puffiness, frothy urine, and hypertension. He gives a history of infection with hepatitis B. Urine examination reveals microscopic hematuria. The histopathological image of the kidney biopsy shows a spike and dome pattern. What is the diagnosis of this condition ?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Pathology
- Pediatric Disorders
- A child presented to the hospital with cola-colored urine, hypertension, and puffiness of eyes. Laboratory investigations were done, and creatinine was 2.5 mg/dL. Treatment was started, and despite treatment, the patient did not improve for the next 3 weeks. The creatinine value increased to 4.5 mg/dL. Which among the following electron microscopic findings will be seen in this patient ?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Pathology
- Pediatric Disorders
- A 3-month-old baby presents with jaundice and clay-coloured stools. Lab investigation reveals that the baby has conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. The liver biopsy shows periductal proliferation. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Pediatrics
- Pediatric Disorders
- An infant is brought with complaints of excessive watering of the eyes and photophobia. The image is given below. What is the likely diagnosis ?

- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Ophthalmology
- Pediatric Disorders
Chloride level in sweat is used in the diagnosis of which disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Pediatrics
- Pediatric Disorders
View More Questions
Questions Asked in NEET PG exam
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for the motor innervation of the muscles of mastication?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The normal pH of arterial blood is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
Which enzyme is deficient in Gaucher’s disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is monitored using:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The causative agent of malaria is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
View More Questions