'X' is: 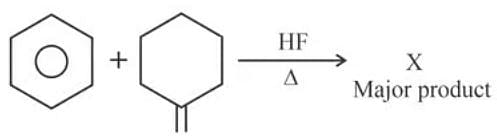

Show Hint
Remember Markovnikov’s rule for electrophilic addition reactions. The most stable carbocation intermediate leads to the major product.
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
Step 1: Identify the Reactants
The reactants are tetrahydrofuran (THF) and 2-methylpropene. The reaction is catalyzed by HF and takes place under heat.
Step 2: Determine the Reaction Mechanism
This reaction is an electrophilic addition of THF to the alkene. HF protonates the alkene to form a carbocation. The oxygen in THF acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation. Finally, deprotonation occurs to yield the product.
Step 3: Determine the Major Product
The major product is determined by Markovnikov’s rule, which states that the proton adds to the carbon of the double bond with more hydrogens. In this case, the carbocation will form on the more substituted carbon of 2-methylpropene, leading to product (1).
Top Questions on Hydrocarbons
Consider the following reaction sequence.

- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- $\text{C}_3\text{H}_6\text{Cl}_2$ (X) $\xrightarrow[\Delta]{\text{NaNH}_2 (2 \text{eq})}$ (Y) $\xrightarrow[\text{(ii) NaBH}_4]{\text{(i) Hg(OAc)}_2/\text{H}_2\text{O}}$ $\text{CH}_3\text{COCH}_3$. (Y) $\xrightarrow[\Delta]{\text{Fe/tube}}$ (Z).
Statement-I : Y gives yellow ppt. with $\text{NaOH}/\text{I}_2$.
Statement-II : Two types of H-atoms and one aromatic ring is present in Z and ratio of Z and X is 1 : 3.
Choose the correct option.- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Ph-CH=CH$_2 \xrightarrow[\text{(PhCOO)}_2]{\text{HBr}}$ Product.
Correct statement(s) regarding product :
(a) Ph-CH(Br)-CH$_3$ is minor product
(b) Benzene is also form a bi product
(c) Reaction follow free radical mechanism
(d) In absence of peroxide carbocation mechanism is followed- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Correct stability order of alkene ::

- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Hydroxy compound ($\text{A}$) with molecular mass $= 122$ react with excess of acetic anhydride and gives compound ($\text{X}$) with molecular mass $= 290$, then find the no. of hydroxy groups in given compound ($\text{A}$).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Concepts Used:
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons can be described as organic compounds that consists only hydrogen and carbon atoms. These compounds are of different types and thereby have distinct natures. Hydrocarbons are colorless gases and are known for discharging faint odours. These have been categorized under four major classes named as alkynes, alkanes, alkenes, and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Types of Hydrocarbons
- Saturated hydrocarbons - Saturated hydrocarbons are those compounds where there is a single bond exists between carbon atoms and are saturated with atoms of hydrogen.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons - Hydrocarbons comprises of at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms are known as unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- Aliphatic hydrocarbons - The term denotes the hydrocarbons formed as an outcome of the chemical degradation of fats. Aliphatic hydrocarbons are basically chemical compounds.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons - They are distinguished because of the presence of benzene rings in them. They give away distinct types of aroma. These hydrocarbons comprises of only hydrogen and carbon atoms.



