Question:
Which of the following has ATP-ase activity in flagella
Which of the following has ATP-ase activity in flagella
Updated On: Mar 10, 2025
- Tubulin
- Kinetosome
- Dynein arms
- Actin
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
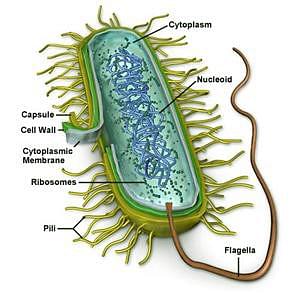
- Dynein arms are intricate structures composed of units of dynein proteins, which function as ATPases, enzymes responsible for hydrolyzing ATP to produce energy.
- These dynein arms are found in the flagella of various organisms, ranging from single-celled organisms like Paramecium to multicellular organisms like humans (in sperm cells).
- Each flagellum possesses dynein arms, which utilize ATP hydrolysis to generate energy.
- This energy is then transmitted through microtubules, ultimately facilitating the forward movement of the flagella.
- Consequently, dynein arms and their ATPase activity play a pivotal role in the motility of organisms.
Was this answer helpful?
3
2
Top Questions on Kingdom Monera
- In which of the following animals, does the digestive tract have additional chambers like crop and gizzard?
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Kingdom Monera
- Component of cytoskeleton present in a cell are
- WBJEE JENPAS UG - 2022
- Biology
- Kingdom Monera
- In which era reptiles were dominated?
- WBJEE JENPAS UG - 2022
- Biology
- Kingdom Monera
- Which one of the following malarial parasite has the longest incubation period?
- WBJEE JENPAS UG - 2022
- Biology
- Kingdom Monera
- Identify the diagram of heterocyst.
- JIPMER - 2019
- Biology
- Kingdom Monera
View More Questions
Questions Asked in TS EAMCET exam
- A body is projected vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Calculate the maximum height reached by the body. (Take \( g = 9.8 \, \text{m/s}^2 \))
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Kinematics
- The properties required for a material to be used as the core of an electromagnet are:
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Magnetism and matter
- Which of the following statements are correct?
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Colligative Properties
- At 27$^\circ$C, 100 mL of 0.05 M Cu$^{2+}$ solution is added to 1 L of 0.1 M KI. Find [KI] in resultant solution.
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
- 4.0 g of a mixture containing Na₂CO₃ and NaHCO₃ is heated to 673K. Loss in mass of the mixture is found to be 0.62g. The percentage of sodium carbonate in the mixture is
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Kingdom Monera
Characteristics of Monera Kingdom
The organisms in this kingdom have the following characteristics: -
- Monerans are single-celled creatures.
- The cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan and is stiff.
- Binary fission is asexual reproduction.
- They have 70S ribosomes in them.
- The locomotory organ is the flagella.
- Organelles such as mitochondria, lys
- osomes, plastids, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, centrosome, and others are not present.
- These are decomposers and mineralizers for the environment