Which among the following option is the correct graphical representation of Boyle's Law?
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
Boyle's Law is a fundamental principle in chemistry and physics that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It can be mathematically expressed as:
PV = k
Where:
- P is the pressure of the gas.
- V is the volume of the gas.
- k is a constant.
Boyle's Law implies that pressure and volume are inversely proportional when temperature is held constant. This means if the volume increases, the pressure decreases, and vice versa, as long as the temperature does not change. The graphical representation of this inverse relationship is a curve (hyperbola) that starts high and slopes downwards, suggesting that when one parameter increases, the other decreases.
The correct option displays a graph of Pressure (P) versus Volume (V) showing a downward curve, which is characteristic of this inverse relationship.
Approach Solution -2
Boyle's law states:
P ∝ \(\frac {1}{V}\)
And at a specific pressure:
P ∝ T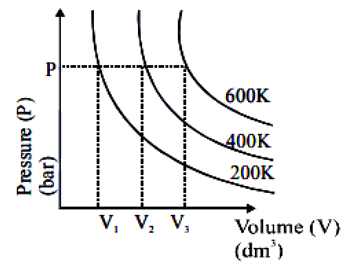
Therefore, The correct option is (B)
Top Questions on States of matter
- Statement-1: Sublimation is a purification technique that is used to separate those solid substances which change from solid to vapor state without passing through liquid state.
Statement-2: If external atmospheric pressure is reduced, then boiling point of substance decreases.
Which of the following is correct?
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- Given below are two statements: Statement I: Sublimation is a purification technique that is used to separate those solid substances which change from solid to vapour state without passing through liquid state. Statement II: If external atmospheric pressure is reduced, then boiling point of a substance is decreased. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct option.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- $10^{-6} \text{ M } \text{NaOH}$ is diluted 100 times. The $\text{pH}$ of the diluted base is:
- LPUNEST - 2026
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- $1.0 \times 10^{-4} \text{ M } \text{HCl}$ is diluted 10 times. The $\text{pH}$ of the final solution is:
- LPUNEST - 2026
- Chemistry
- States of matter
- What is the relation between \( \Delta G \) and \( E_{\text{cell}} \)?
- GUJCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- States of matter
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
States of Matter
The matter is made up of very tiny particles and these particles are so small that we cannot see them with naked eyes.
There are three States of Matter:
The three states of matter are as follows:
Solid State:
- The solid-state is one of the fundamental states of matter.
- Solids differ from liquids and gases by the characteristic of rigidity.
- The molecules of solids are tightly packed because of strong intermolecular forces; they only oscillate about their mean positions.
Liquid State:
- The molecules in a liquid are closely packed due to weak intermolecular forces.
- These forces are weaker than solids but stronger than that of gases.
- There is much space in between the molecules of liquids which makes their flowing ability easy.
Gaseous State:
- In this state of matter, distances between the molecules are large (intermolecular distance is in the range of 10-7-10-5 cm.
- The intermolecular forces experienced between them are negligible.
- Thus, translatory, rotatory and vibratory motions are observed prominently in gases.



