What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Solution and Explanation
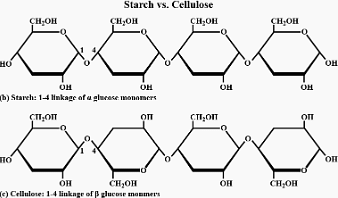
Starch consists of two components - amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a long linear chain of ∝-D-(+)-glucose units joined by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage (∝-link).
Amylopectin is a branched-chain polymer of ∝-D-glucose units, in which the chain is formed by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage and the branching occurs by C1-C6 glycosidic linkage.
On the other hand, cellulose is a straight-chain polysaccharide of β-D-glucose units joined by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage (β-link).
Top Questions on Biomolecules
- Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents:
(a) HCN
(b) Br\(_2\) water- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- Which vitamin is responsible for the coagulation of blood?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- Which one of the following is a disaccharide?
\[ \text{Glucose, Lactose, Amylose, Fructose} \]- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
- What is the difference between native protein and denatured protein?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Biomolecules
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
- Write the cell reaction and calculate the e.m.f. of the following cell at 298 K:
\[ \text{Sn}(s) \mid \text{Sn}^{2+} (\text{0.004 M}) \parallel \text{H}^+ (\text{0.02 M}) \mid \text{H}_2 (\text{1 Bar}) \mid \text{Pt}(s) \]
(Given: \( E^\circ_{\text{Sn}^{2+}/\text{Sn}} = -0.14 \, \text{V}, E^\circ_{\text{H}^+/\text{H}_2} = 0.00 \, \text{V} \))- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Electrochemistry
If vector \( \mathbf{a} = 3 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} - \hat{k} \) \text{ and } \( \mathbf{b} = \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} \), then which of the following is correct?
- Find the value of $x$, if \[ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 & 2 \\ 2 & 5 & 1 \\ 15 & 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ x \\ 2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \]
- Two point charges of \( -5\,\mu C \) and \( 2\,\mu C \) are located in free space at \( (-4\,\text{cm}, 0) \) and \( (6\,\text{cm}, 0) \) respectively.
(a) Calculate the amount of work done to separate the two charges at infinite distance.
(b) If this system of charges was initially kept in an electric field \[ \vec{E} = \frac{A}{r^2}, \text{ where } A = 8 \times 10^4\, \text{N}\,\text{C}^{-1}\,\text{m}^2, \] calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the system.- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Electrostatics
- 4,000 shares of ₹ 10 each were forfeited for non-payment of second and final call money of ₹ 2 per share. The minimum amount that the company must collect at the time of reissue of these shares will be :
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Accounting for Share Capital
Concepts Used:
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are the most abundant hydrocarbons that exist in our food. They are long chains of hydrocarbons inclusive of smaller units called monosaccharides or monomers, related to each other through glycosidic linkages. Cellulose, starch, chitin, and glycogen are the most common polysaccharides found in food.
Characteristics of Polysaccharides:
- Desiccation does not cause Polysaccharides to structure crystals.
- They do not have a candied flavor.
- Water cannot infiltrate the molecules due to the numerous hydrogen bonds, making them hydrophobic.
- They are osmotically inactive and close-packed inside the cells. Many are water-insoluble.
- They are collections of hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. 2:1 is the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen.
- They are carbohydrates with a molecular weight comparatively more excessive than other compounds. It is also possible to extract a white powder out of it.
Types of Polysaccharides:
- Homopolysaccharides
- Heteropolysaccharides