The solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt AX2 is 3.2 ×10–11. Its solubility (in moles/liter) is
The solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt AX2 is 3.2 ×10–11. Its solubility (in moles/liter) is
3.1×10–4
2 × 10–4
4 × 10–4
5.6 × 10–6
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
The solubility of the sparingly soluble salt AX2 (with a solubility product of 3.2 × 10⁻¹¹) is 4 × 10⁻⁴ moles/liter.
Top Questions on Thermodynamics
- A cylindrical conductor of length \(2 \, \text{m}\) and area of cross-section \(0.2 \, \text{mm}^2\) carries an electric current of \(1.6 \, \text{A}\) when its ends are connected to a \(2 \, \text{V}\) battery. Mobility of electrons in the conductor is \( \alpha \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m}^2\text{/V s}. \) The value of \( \alpha \) is ______________.
(Electron concentration \(= 5 \times 10^{28} \, \text{m}^{-3}\), electron charge \(= 1.6 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{C}\))- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Thermodynamics
- An insulated cylinder of volume \(60\,\text{cm}^3\) is filled with a gas at \(27^\circ\text{C}\) and \(2\) atmospheric pressure. The gas is then compressed making the final volume \(20\,\text{cm}^3\) while allowing the temperature to rise to \(77^\circ\text{C}\). The final pressure is ____________ atmospheric pressure.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Thermodynamics
- In a Young's double slit experiment set up, the two slits are kept 0.4 mm apart and screen is placed at 1 m from slits. If a thin transparent sheet of thickness 20 $\mu$m is introduced in front of one of the slits then center bright fringe shifts by 20 mm on the screen. The refractive index of transparent sheet is given by $\frac{\alpha{10}$, where $\alpha$ is _________}.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Thermodynamics
- Which of the following solutions is the most acidic?
- LPUNEST - 2026
- Chemistry
- Thermodynamics
- Match List - I with List - II. List - I (Partial Derivatives) \(and\) List - II (Thermodynamic Quantity)

In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Thermodynamics
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
Law of Chemical Equilibrium
Law of Chemical Equilibrium states that at a constant temperature, the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the molar concentrations of the reactants each raised to a power equal to the corresponding stoichiometric coefficients as represented by the balanced chemical equation.
Let us consider a general reversible reaction;
A+B ↔ C+D
After some time, there is a reduction in reactants A and B and an accumulation of the products C and D. As a result, the rate of the forward reaction decreases and that of backward reaction increases.
Eventually, the two reactions occur at the same rate and a state of equilibrium is attained.
By applying the Law of Mass Action;
The rate of forward reaction;
Rf = Kf [A]a [B]b
The rate of backward reaction;
Rb = Kb [C]c [D]d
Where,
[A], [B], [C] and [D] are the concentrations of A, B, C and D at equilibrium respectively.
a, b, c, and d are the stoichiometric coefficients of A, B, C and D respectively.
Kf and Kb are the rate constants of forward and backward reactions.
However, at equilibrium,
Rate of forward reaction = Rate of backward reaction.
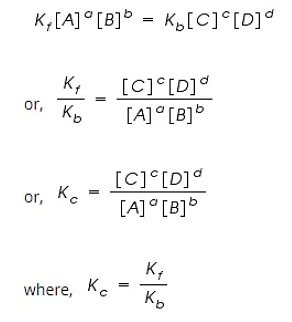
Kc is called the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of molar concentrations.
The above equation is known as the equation of Law of Chemical Equilibrium.