The solubility of \( \text{PbI}_2 \) in 0.10 M KI(aq) is ........... \( \times 10^{-7} \) M (rounded up to two decimal places).
\(\text{[The solubility product, \( K_{\text{sp}} = 7.1 \times 10^{-9} \)]}\)
The solubility of \( \text{PbI}_2 \) in 0.10 M KI(aq) is ........... \( \times 10^{-7} \) M (rounded up to two decimal places).
\(\text{[The solubility product, \( K_{\text{sp}} = 7.1 \times 10^{-9} \)]}\)
Show Hint
Correct Answer: 7 - 7.2
Solution and Explanation
To find the solubility of \( \text{PbI}_2 \) in 0.10 M KI(aq), we start with the dissolution equation:
\(\text{PbI}_2(s) \rightleftharpoons \text{Pb}^{2+}(aq) + 2\text{I}^-(aq)\)
The solubility product (\( K_{\text{sp}} \)) is given as \(7.1 \times 10^{-9}\). When \( \text{PbI}_2 \) dissolves, let the solubility be \( s \). In a 0.10 M KI solution, the concentration of \(\text{I}^-\) is increased by the dissociation of KI to 0.10 M. Therefore, the equilibrium concentrations are \([\text{Pb}^{2+}] = s\) and \([\text{I}^-] = 0.10 + 2s \approx 0.10\) since \(s\) is small.
Substitute into the \( K_{\text{sp}} \) expression:
\( K_{\text{sp}} = [\text{Pb}^{2+}][\text{I}^-]^2 = s \times (0.10)^2\)
\(7.1 \times 10^{-9} = s \times 0.01\)
Solving for \(s\):
\(s = \frac{7.1 \times 10^{-9}}{0.01} = 7.1 \times 10^{-7} \, \text{M}\)
Answer: \(7.1 \times 10^{-7}\, \text{M}\)
Top Questions on Chemical equilibria
- The ratio of osmotic pressures of aqueous solutions of 0.01 M BaCl2 to 0.005 M NaCl is
[Given: Both compounds dissociate completely in water]- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- A 1.0 L solution is prepared by dissolving 2.0 g of benzoic acid and 4.0 g of sodium benzoate in water. The pH of the resulting solution is _______. (rounded off to one decimal place)
Given: Molar mass of benzoic acid is 122 g mol−1
Molar mass of sodium benzoate is 144 g mol−1
p𝐾a of benzoic acid is 4.2- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- 0.1 M aqueous solution of a weak monobasic acid has pH 2.0. The pKa of the monobasic acid is _______. (rounded off to one decimal place)
- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- Consider the exothermic chemical reaction O2(𝑔)+2H2(𝑔) ⇌ 2H2O(𝑔) at equilibrium in a closed container. The correct statement(s) is/are
- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- The isoelectric point of glutamic acid is ______.
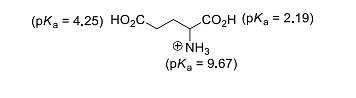
(round off to two decimal places)- IIT JAM CY - 2023
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
Questions Asked in IIT JAM CY exam
- Among the following, the correct condition(s) for spontaneity is(are)
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas starting from state A, goes through B and C to state D, as shown in the figure. Total change in entropy (in J K\(^{-1}\)) during this process is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
The number of chiral carbon centers in the following molecule is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
- Consider the following matrices A and B.
\[ A = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 2 & 0 & 0 \\ 3 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 5 & 5 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 6 & 7 \\ 0 & 0 & 8 & 9 \end{pmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad B = \begin{pmatrix} 10 & 11 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 12 & 13 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 15 & 16 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 17 & 18 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
If \( C = AB \), the sum of the diagonal elements of \( C \) is ..............
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
A tube fitted with a semipermeable membrane is dipped into 0.001 M NaCl solution at 300 K as shown in the figure. Assume density of the solvent and solution are the same. At equilibrium, the height of the liquid column \( h \) (in cm) is .........

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry