The isoelectric point of glutamic acid is ______.
(round off to two decimal places)

(round off to two decimal places)
Correct Answer: 3.21 - 3.23
Solution and Explanation
Isoelectric Point of Glutamic Acid
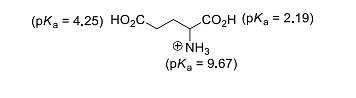
The isoelectric point (\( pI \)) of an amino acid is the pH at which the molecule carries no net electric charge. For glutamic acid, the equation to find \( pI \) involves averaging the \( pK_a \) values of the acidic groups:
Step 1: Identify the relevant \( pK_a \) values for deprotonation:
- \( pK_{a1} \) (α-carboxyl group) = 2.19
- \( pK_{a2} \) (side-chain carboxyl group) = 4.25
Step 2: Compute the average of these values for \( pI \):
The equation for \( pI \) is:
\[ pI = \frac{pK_{a1} + pK_{a2}}{2} = \frac{2.19 + 4.25}{2} = 3.22 \]
Step 3: Verify the result:
The computed \( pI \) value of 3.22 is within the specified range of 3.21 to 3.23, confirming its correctness.
Final Answer:
Thus, the isoelectric point of glutamic acid, rounded to two decimal places, is 3.22.
Top Questions on Chemical equilibria
- The ratio of osmotic pressures of aqueous solutions of 0.01 M BaCl2 to 0.005 M NaCl is
[Given: Both compounds dissociate completely in water]- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- A 1.0 L solution is prepared by dissolving 2.0 g of benzoic acid and 4.0 g of sodium benzoate in water. The pH of the resulting solution is _______. (rounded off to one decimal place)
Given: Molar mass of benzoic acid is 122 g mol−1
Molar mass of sodium benzoate is 144 g mol−1
p𝐾a of benzoic acid is 4.2- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- 0.1 M aqueous solution of a weak monobasic acid has pH 2.0. The pKa of the monobasic acid is _______. (rounded off to one decimal place)
- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- Consider the exothermic chemical reaction O2(𝑔)+2H2(𝑔) ⇌ 2H2O(𝑔) at equilibrium in a closed container. The correct statement(s) is/are
- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
- The volume of water (in mL) required to be added to a 100 mL solution (aq. 0.1 M) of a weak acid (HA) at 25 °C to double its degree of dissociation is
[Given: Ka of HA at 25 °C=1.8 x10−5 ]- IIT JAM CY - 2023
- Physical Chemistry
- Chemical equilibria
Questions Asked in IIT JAM CY exam
- Among the following, the correct condition(s) for spontaneity is(are)
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas starting from state A, goes through B and C to state D, as shown in the figure. Total change in entropy (in J K\(^{-1}\)) during this process is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
The number of chiral carbon centers in the following molecule is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
- Consider the following matrices A and B.
\[ A = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 2 & 0 & 0 \\ 3 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 5 & 5 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 6 & 7 \\ 0 & 0 & 8 & 9 \end{pmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad B = \begin{pmatrix} 10 & 11 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 12 & 13 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 15 & 16 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 17 & 18 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
If \( C = AB \), the sum of the diagonal elements of \( C \) is ..............
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
A tube fitted with a semipermeable membrane is dipped into 0.001 M NaCl solution at 300 K as shown in the figure. Assume density of the solvent and solution are the same. At equilibrium, the height of the liquid column \( h \) (in cm) is .........

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry