Question:
The relationship between ionization and change in concentration of any weak electrolyte is represented as:
The relationship between ionization and change in concentration of any weak electrolyte is represented as:
Updated On: Aug 1, 2022
- $\alpha=\frac{K_{a}}{C}$
- $\alpha=\sqrt{\frac{K_{a}}{C}}$
- $\alpha=K_{a} \cdot C$
- $\alpha=\frac{\sqrt{K_{a}}}{C^{2}}$
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
The relationship between ionisation and change in concentration of any weak electrolyte is represented by $\alpha=\sqrt{\frac{K a}{C}}$
where $\alpha=$ degree of dissociation
$C=$ molar concentration
$K_{a}=$ ionisation constant
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on kinetics equations
- Magnetic Moment of \( \text{Mn}^{2+} \) is:
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
Find the time required to complete a reaction 90% if the reaction is completed 50% in 15 minutes.
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
- IUPAC Name of Glyceraldehyde is:
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
- IUPAC Name of Acetone is:
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
- The half-life period of a first order reaction is 1000 seconds. Its rate constant is:
- KEAM - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
View More Questions
Questions Asked in Rajasthan PMT exam
- 300 cal of heat is supplied to raise the temperature of 50 g of air from $ 20{}^\circ C $ to $ 30{}^\circ C $ without any change in its volume. Change in internal energy per gram of air is
- Rajasthan PMT - 2011
- internal energy
- The velocity of water flowing in a non-uniform tube is 20 cm/s at a point where the tube radius is 0.2 cm. The velocity at another point, where the radius is 0.1 cm, is
- Rajasthan PMT - 2011
- mechanical properties of fluid
- Block A of mass 4 kg and block B of mass 6 kg are resting on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure. There is no friction between the block B and the horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the blocks is 0.2. If the value of $ g=10\,m/{{s}^{2}}, $ the maximum horizontal force F that can be applied on block B without any relative motion between A and B is
- The excess pressure inside a soap bubble A is twice that in another soap bubble B. The ratio of volumes of A and B is
- Rajasthan PMT - 2011
- Surface Tension
- The unit of surface tension is
- Rajasthan PMT - 2011
- Surface Tension
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Kinetics Equations
It is branch of physics that defines motion with respect to space and time is known as kinematics.
Inverse Kinematics: Inverse Kinematics do the reverse of kinematics.
There are four basic kinematics equations:
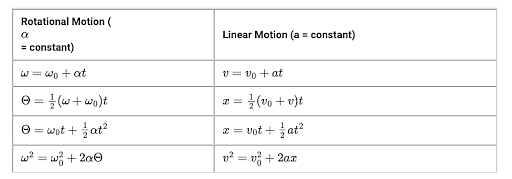
Rotational Kinematics Equations
Another branch of kinematics equations which deals with the rotational motion of anybody.