Question:
Magnetic Moment of \( \text{Mn}^{2+} \) is:
Magnetic Moment of \( \text{Mn}^{2+} \) is:
Show Hint
The magnetic moment depends on the number of unpaired electrons, calculated using \( \mu = \sqrt{n(n+2)} \, \text{BM} \), where \( n \) is the number of unpaired electrons.
Updated On: Jan 13, 2026
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Solution and Explanation
Step 1: Determine the number of unpaired electrons. The electronic configuration of \( \text{Mn}^{2+} \) is: \[ \text{[Ar]} \, 3d^5 \] This indicates 5 unpaired electrons in the \( 3d \) subshell.
Step 2: Use the formula for magnetic moment. The magnetic moment \( \mu \) is given by: \[ \mu = \sqrt{n(n+2)} \, \text{BM}, \] where \( n \) is the number of unpaired electrons.
\[ \mu = \sqrt{5(5+2)} = \sqrt{35} = 5.9 \, \text{BM}. \] Hence, the magnetic moment of \( \text{Mn}^{2+} \) is 5.9 BM.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on kinetics equations
Find the time required to complete a reaction 90% if the reaction is completed 50% in 15 minutes.
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
- IUPAC Name of Glyceraldehyde is:
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
- IUPAC Name of Acetone is:
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
- The half-life period of a first order reaction is 1000 seconds. Its rate constant is:
- KEAM - 2024
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
- If the distribution of molecular speeds of a gas is as per the figure shown below, then the ratio of the most probable, the average, and the root mean square speeds, respectively, is
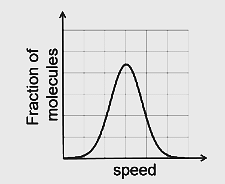
- JEE Advanced - 2020
- Chemistry
- kinetics equations
View More Questions
Questions Asked in MHT CET exam
Which part of root absorb mineral?
- MHT CET - 2025
- The Root
- A body of mass 2 kg is moving in a circular path of radius 3 m with a constant speed of 6 m/s. What is the centripetal force acting on the body?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Centripetal forces
- A 200 g sample of water at 80°C is mixed with 100 g of water at 20°C. Assuming no heat loss to the surroundings, what is the final temperature of the mixture?
- MHT CET - 2025
- thermal properties of matter
- Given the equation: \[ 81 \sin^2 x + 81 \cos^2 x = 30 \] Find the value of \( x \).
- MHT CET - 2025
- Trigonometric Identities
- A body of mass 10 kg is at a height of 5 m above the surface of the Earth. What is the gravitational potential energy of the body? (Take \( g = 10 \, \text{m/s}^2 \))
- MHT CET - 2025
- Gravitational Potential Energy
View More Questions