Spongiform encephalopathy is caused by
- Virus
- Fungus
- Prion
- E. coli
The Correct Option is C
Approach Solution - 1
Approach Solution -2
Ans. The family of uncommon progressive neurodegenerative brain illnesses known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) or prion diseases affects both humans and animals. They invariably result in death and have protracted incubation periods before symptoms appear. Prions, improperly folded proteins, which accumulate in the brain and produce brain damage and the disease's recognizable symptoms, are thought to be the cause of TSEs.
- The neurological condition in cattle known as bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), sometimes referred to as mad cow disease, is brought on by prions.
- Prions are defective protein molecules that may spread their erroneous structure to other versions of the same protein, making them contagious.
- A degenerative neurologic condition affecting cows is called BSE.
- Progressive denotes a problem that worsens with time.
- The term "neurologic" refers to injury to the brain and spinal cord of the cow's central nervous system.
- The healthy prion protein transforms into a dangerous, aberrant form.
- The aberrant prion is completely unknown to the ill cow's body.
- The illness cannot be fought off by the cow's body if it is unaware that it is there.
- Incoordination is a typical indication of BSE in cows.
- An ill cow has difficulty standing and walking.
- As a sick cow may sometimes exhibit extremely agitated or aggressive behavior, BSE is frequently referred to as "mad cow disease."
- When a cow contracts the aberrant prion, it typically takes four to six years before it begins to exhibit BSE symptoms.
- The incubation phase is what we refer to as.
- A cow's BSE cannot be detected by gazing at it during the incubation stage.
- A cow generally succumbs to the illness between two weeks to six months of first exhibiting signs.
- BSE has no known cure, and there is no vaccination to protect against it.
- There is currently no accurate method for testing for BSE in a live cow.
- When examining a cow's brain tissue under a microscope after it has passed away, researchers can determine if it has BSE by observing the spongy texture.
Learn with videos:
Top Questions on biological classification
- Which of the following microorganisms is used in the production of curd from milk?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- In a DNA molecule, which of the following base-pairings is correct?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- Which is not a prime element?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- Study the following and choose the incorrect combinations:
I. Phylum: Porifera, Special cells: Lasso cells, Example: Spongilla
II. Phylum: Cnidaria, Special cells: Stinging cells, Example: Hydra
III. Phylum: Ctenophora, Special cells: Choanocytes, Example: Pleurobrachia
IV. Phylum: Platyhelminthes, Special cells: Flame cells, Example: Fasciola- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- biological classification
- Study the following and choose the correct combinations:

- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- biological classification
Questions Asked in COMEDK UGET exam
- Given that the freezing point of benzene is $ 5.48^\circ C $ and its $ K_f $ value is $ 5.12^\circ C/m $, what would be the freezing point of a solution of 20 g of propane in 400 g of benzene?
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Colligative Properties
200 ml of an aqueous solution contains 3.6 g of Glucose and 1.2 g of Urea maintained at a temperature equal to 27$^{\circ}$C. What is the Osmotic pressure of the solution in atmosphere units?
Given Data R = 0.082 L atm K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$
Molecular Formula: Glucose = C$_6$H$_{12}$O$_6$, Urea = NH$_2$CONH$_2$- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Colligative Properties
- An inorganic compound W undergoes the following reactions: $ W + \text{Na}_2\text{CO}_3 \xrightarrow{\text{O}_2 / \text{heat}} X + H^+ \xrightarrow{} Y(s) $ $ Y(aq) + \text{KCl} (aq) \xrightarrow{} Z(s) $ Z appears in the form of orange crystals and is used as an oxidising agent in acid medium. Identify the compound W.
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- coordination compounds
- A current of 3.0 A is passed through 750 ml of 0.45 M solution of CuSO₄ for 2 hours with a current efficiency of 90\%. If the volume of the solution is assumed to remain constant, what would be the final molarity of CuSO₄ solution?
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Solutions
- For a reaction $ 5X + Y \to 3Z $, the rate of formation of Z is $ 2.4 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{mol L}^{-1} \text{s}^{-1} $. Calculate the average rate of disappearance of X.
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
Concepts Used:
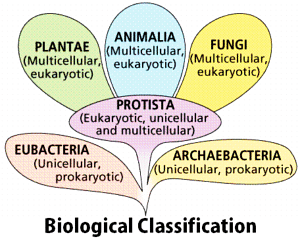
Biological Classification
The process of grouping living organisms into categories is called biological classification. The most modern 5-kingdom classification was put ahead by an eminent scientist R.H.Whittaker. The five-kingdom classification is based on the criteria like cell structure, mode of nutrition, body form, and reproduction. One of the most important characteristics of this system is that it follows the evolutionary sequence of living organisms. The organisms are classified into distinct taxa or levels like Kingdom, Phylum, Division, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. The 5 kingdoms are as follows: