Let S be the sample space of all five digit numbers. It p is the probability that a randomly selected number from S, is multiple of 7 but not divisible by 5, then 9p is equal to
Let S be the sample space of all five digit numbers. It p is the probability that a randomly selected number from S, is multiple of 7 but not divisible by 5, then 9p is equal to
- 1.0146
- 1.2085
- 1.0285
- 1.1521
The Correct Option is C
Approach Solution - 1
To solve this problem, we need to calculate the probability \( p \) that a randomly selected five-digit number is a multiple of 7 but not divisible by 5. We then multiply this probability by 9 to find \( 9p \).
- Determine the range of five-digit numbers. The smallest five-digit number is 10000 and the largest is 99999.
- Calculate the total number of five-digit numbers, which is: \(99999 - 10000 + 1 = 90000\)
- Find the first and last five-digit numbers that are multiples of 7:
- The smallest five-digit number divisible by 7 is calculated as follows: \(10000 \div 7 \approx 1428.57\). Rounding up gives us 1429, so \(1429 \times 7 = 10003\).
- The largest five-digit number divisible by 7 is calculated as follows: \(99999 \div 7 \approx 14285.57\). Rounding down gives us 14285, so \(14285 \times 7 = 99995\).
- Calculate the number of multiples of 7: \(14285 - 1429 + 1 = 12857\)
- Next, find the multiples of 35 (since they are both multiples of 7 and 5):
- The smallest five-digit number divisible by 35 is: \(10000 \div 35 \approx 285.71\). Rounding up gives 286, \(286 \times 35 = 10010\).
- The largest five-digit number divisible by 35 is: \(99999 \div 35 \approx 2857.11\). Rounding down gives 2857, \(2857 \times 35 = 99995\).
- Calculate the number of multiples of 35: \(2857 - 286 + 1 = 2572\)
- Calculate the number of five-digit numbers that are multiples of 7 but not multiples of 5: \(12857 - 2572 = 10285\)
- Determine the probability \( p \): \(p = \frac{10285}{90000}\)
- Compute \( 9p \): \(9p = 9 \times \frac{10285}{90000} = \frac{92565}{90000} \approx 1.0285\)
The value of \( 9p \) is approximately 1.0285, which corresponds to the correct answer.
Approach Solution -2
The correct answer is (C):
Among the 5 digit numbers,
First number divisible by 7 is 10003 and last is 99995.
⇒ Number of numbers divisible by 7.
= \(\frac{99995-10003}{7} + 1\)
= 12875
First number divisible by 35 is 10010 and last is 99995.
⇒ Number of numbers divisible by 35 =\(\frac{ 99995-10010}{35}+1 = 2572\)
Hence number of number divisible by 7 but not by 5
= 12857 – 2572
= 10285
9P =\( \frac{10285}{90000} × 9\)
= 1.0285
Top Questions on types of differential equations
- Let the system of equations \(x+2y+3z = 5\), \(2x+3y+z = 9\), \(4x+3y+λz = μ\) have an infinite number of solutions. Then \(λ + 2μ\) is equal to
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
- If \( m_1 \) and \( m_2 \) are the slopes of the direct common tangents drawn to the circles \[ x^2 + y^2 - 2x - 8y + 8 = 0 \quad \text{and} \quad x^2 + y^2 - 8x + 15 = 0 \] then \( m_1 + m_2 \) is:
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
- If \( (2,3) \) is the focus and \( x - y + 3 = 0 \) is the directrix of a parabola, then the equation of the tangent drawn at the vertex of the parabola is:
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
- If the focus of an ellipse is \((-1,-1)\), equation of its directrix corresponding to this focus is \(x + y + 1 = 0\) and its eccentricity is \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\), then the length of its major axis is:
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
- The equation of the common tangent to the parabola \(y^2 = 8x\) and the circle \(x^2 + y^2 = 2\) is \(ax + by + 2 = 0\). If \(-\frac{a}{b}>0\), then \(3a^2 + 2b + 1 =\)
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Mathematics
- types of differential equations
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- A 20 m long uniform copper wire held horizontally is allowed to fall under the gravity (g = 10 m/s²) through a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.5 Gauss perpendicular to the length of the wire. The induced EMF across the wire when it travels a vertical distance of 200 m is_______ mV.}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Thermodynamics
- If the end points of chord of parabola \(y^2 = 12x\) are \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) and it subtend \(90^\circ\) at the vertex of parabola then \((x_1x_2 - y_1y_2)\) equals :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Probability
- The sum of all possible values of \( n \in \mathbb{N} \), so that the coefficients of \(x, x^2\) and \(x^3\) in the expansion of \((1+x^2)^2(1+x)^n\) are in arithmetic progression is :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Integration
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
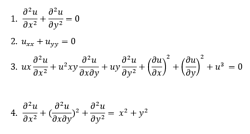
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
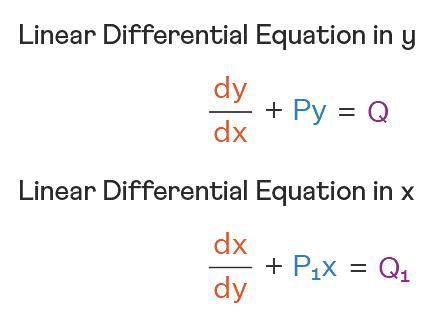
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations