Let \(\alpha\ and\ \beta\) be real numbers such that \(-\frac{\pi}{4}<\beta<0<\alpha<\frac{\pi}{4}\). If \(\sin (\alpha+\beta)=\frac{1}{3}\ and\ \cos (\alpha-\beta)=\frac{2}{3}\), then the greatest integer less than or equal to
\(\left(\frac{\sin \alpha}{\cos \beta}+\frac{\cos \beta}{\sin \alpha}+\frac{\cos \alpha}{\sin \beta}+\frac{\sin \beta}{\cos \alpha}\right)^2\) is ____
Let \(\alpha\ and\ \beta\) be real numbers such that \(-\frac{\pi}{4}<\beta<0<\alpha<\frac{\pi}{4}\). If \(\sin (\alpha+\beta)=\frac{1}{3}\ and\ \cos (\alpha-\beta)=\frac{2}{3}\), then the greatest integer less than or equal to
\(\left(\frac{\sin \alpha}{\cos \beta}+\frac{\cos \beta}{\sin \alpha}+\frac{\cos \alpha}{\sin \beta}+\frac{\sin \beta}{\cos \alpha}\right)^2\) is ____
Correct Answer: 1
Solution and Explanation
\(\sin(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{1}{3}\) and \(\cos(\alpha - \beta) = \frac{2}{3}\)
The expression to simplify is:
\(\left(\frac{\sin \alpha}{\cos \beta} + \frac{\cos \beta}{\sin \alpha} + \frac{\cos \alpha}{\sin \beta} + \frac{\sin \beta}{\cos \alpha}\right)^2\)
This expression is equal to:
\(\left(\frac{\cos(\alpha - \beta)}{\sin \beta \cos \beta} + \frac{\cos(\alpha - \beta)}{\sin \alpha \cos \alpha}\right)^2\)
This can be simplified further to:
\(= \left(\frac{4}{3} \left\{\frac{1}{\sin 2\beta} + \frac{1}{\sin 2\alpha}\right\}\right)^2\)
Next, simplifying more:
\(= \frac{16}{9}\left(\frac{2 \sin(\alpha + \beta) \cos(\alpha - \beta)}{\sin 2\alpha \sin 2\beta}\right)^2\)
This becomes:
\(= \frac{16}{9} \left(\frac{4 \times \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{2}{3}}{\cos(2\alpha - 2\beta) - \cos(2\alpha + 2\beta)}\right)^2\)
We simplify the denominator further:
\(= \frac{16}{9} \left(\frac{\frac{8}{9}}{2 \cos^2(\alpha - \beta) - 1 - 1 + 2 \sin^2(\alpha + \beta)}\right)^2\)
This simplifies to:
\(= \frac{16}{9} \left(\frac{\frac{8}{9}}{\frac{8}{9} + 2 + \frac{2}{9}}\right)\)
Finally, we get:
\(= \frac{16}{9} = 1\)
Therefore, the correct answer is 1.
Top Questions on Some Applications of Trigonometry
- If \[ \frac{\cos^2 48^\circ - \sin^2 12^\circ}{\sin^2 24^\circ - \sin^2 6^\circ} = \frac{\alpha + \sqrt{5\beta}}{2} \] then the value of \( (\alpha + \beta) \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
- The number of values of \( x \) satisfying \( \tan^{-1}(4x) + \tan^{-1}(6x) = \frac{\pi}{6} \) and \( x<\left[ \frac{-1}{2\sqrt{6}} , \frac{1}{2\sqrt{6}} \right] \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
- The number of solutions of the equation \( \tan 3x = \cot x \) in \( x \in [0, 2\pi] \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
- The minimum value of \( (\sin^{-1} x)^2 + (\cos^{-1} x)^2 \) in \( x \in \left[ \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}, \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right] \) is \( \frac{a \pi^2}{b} \), then \( a + b \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
- The value of cosec10° - √3 sec10°
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Some Applications of Trigonometry
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
Trigonometric Functions
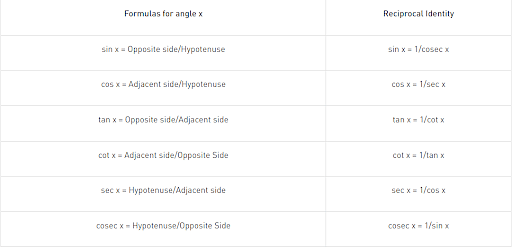
The relationship between the sides and angles of a right-angle triangle is described by trigonometry functions, sometimes known as circular functions. These trigonometric functions derive the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle. In trigonometry, there are three primary functions of sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan). The other three main functions can be derived from the primary functions as cotangent (cot), secant (sec), and cosecant (cosec).
Six Basic Trigonometric Functions:
- Sine Function: The ratio between the length of the opposite side of the triangle to the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
sin x = a/h
- Cosine Function: The ratio between the length of the adjacent side of the triangle to the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
cos x = b/h
- Tangent Function: The ratio between the length of the opposite side of the triangle to the adjacent side length.
tan x = a/b
Tan x can also be represented as sin x/cos x
- Secant Function: The reciprocal of the cosine function.
sec x = 1/cosx = h/b
- Cosecant Function: The reciprocal of the sine function.
cosec x = 1/sinx = h/a
- Cotangent Function: The reciprocal of the tangent function.
cot x = 1/tan x = b/a
Formulas of Trigonometric Functions: