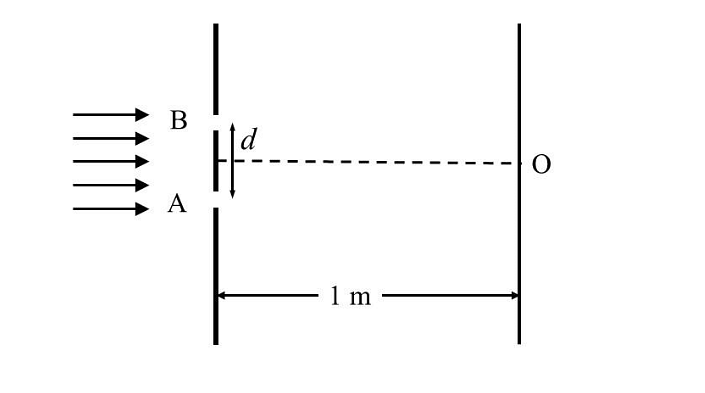
The \(8^{th}\) bright fringe above the point O oscillates with time between two extreme positions. The separation between these two extreme positions, in micrometer (𝜇m), is ______.
Correct Answer: 601.5
Approach Solution - 1
To solve the problem, we need to find the difference between the extreme positions of the 8th bright fringe in a double-slit experiment, where the slit separation varies with time.
1. Understanding the Position of the Bright Fringe:
The position of the \(n^{th}\) bright fringe is given by:
\[
y_n = \frac{n \lambda D}{d}
\]
where \(d\) is the slit separation, \(\lambda\) is the wavelength, \(D\) is the distance to the screen, and \(n = 8\). We are given:
\[
d = (0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \, \text{mm}, \quad D = 1 \, \text{m}, \quad \lambda = 6 \times 10^{-7} \, \text{m}, \quad n = 8
\]
2. Expressing the Position \(y_8\):
Convert units: \(d = (0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m}\). The position of the 8th bright fringe is:
\[
y_8 = \frac{8 \times 6 \times 10^{-7} \times 1}{0.8 \times 10^{-3} + 0.04 \times 10^{-3} \sin \omega t} = \frac{48 \times 10^{-7}}{(0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \times 10^{-3}} = \frac{48 \times 10^{-4}}{0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t} \, \text{m}
\]
3. Finding Extreme Positions:
The term \(0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t\) is minimized when \(\sin \omega t = -1\) and maximized when \(\sin \omega t = 1\).
- Maximum \(y_8\) (when \(\sin \omega t = -1\)):
\[
d = 0.8 - 0.04 = 0.76 \, \text{mm} = 0.76 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m}
\]
\[
y_{8, \text{max}} = \frac{48 \times 10^{-4}}{0.76} = \frac{48 \times 10^{-4}}{76 \times 10^{-2}} = \frac{48}{76} \times 10^{-2} = \frac{12}{19} \times 10^{-2} \, \text{m}
\]
- Minimum \(y_8\) (when \(\sin \omega t = 1\)):
\[
d = 0.8 + 0.04 = 0.84 \, \text{mm} = 0.84 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m}
\]
\[
y_{8, \text{min}} = \frac{48 \times 10^{-4}}{0.84} = \frac{48 \times 10^{-4}}{84 \times 10^{-2}} = \frac{48}{84} \times 10^{-2} = \frac{4}{7} \times 10^{-2} \, \text{m}
\]
4. Calculating the Separation:
The difference between the extreme positions is:
\[
|y_{8, \text{max}} - y_{8, \text{min}}| = \left| \frac{12}{19} - \frac{4}{7} \right| \times 10^{-2}
\]
Compute:
\[
\frac{12}{19} - \frac{4}{7} = \frac{12 \cdot 7 - 4 \cdot 19}{19 \cdot 7} = \frac{84 - 76}{133} = \frac{8}{133}
\]
Thus:
\[
|y_{8, \text{max}} - y_{8, \text{min}}| = \frac{8}{133} \times 10^{-2} \, \text{m}
\]
Convert to micrometers (\(1 \, \text{m} = 10^6 \, \mu\text{m}\)):
\[
\frac{8}{133} \times 10^{-2} \times 10^6 = \frac{8}{133} \times 10^4 = \frac{80000}{133} \approx 601.50 \, \mu\text{m}
\]
5. Final Answer:
The separation between the extreme positions of the 8th bright fringe is approximately \(601.50 \, \mu\text{m}\).
Approach Solution -2
To solve this problem, we analyze how the position of the 8th bright fringe in a Young’s double slit experiment varies with time due to oscillations in the slit separation.
1. Given Data:
- Slit separation as a function of time: \( d(t) = (0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \, \text{mm} \)
- Wavelength of light used: \( \lambda = 6000 \, \text{Å} = 6 \times 10^{-7} \, \text{m} \)
- Distance to the screen: \( D = 1 \, \text{m} \)
- Fringe number: \( n = 8 \)
2. Formula for Fringe Position:
The position of the \( n^{\text{th}} \) bright fringe from the central fringe is given by:
\[
y_n = \frac{n \lambda D}{d}
\]
Since the slit separation \( d \) varies with time, the position \( y_n \) will also vary with time accordingly.
3. Determine the Extreme Slit Separations:
The slit separation oscillates between:
- Minimum: \( d_{\text{min}} = 0.8 - 0.04 = 0.76 \, \text{mm} = 0.76 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m} \)
- Maximum: \( d_{\text{max}} = 0.8 + 0.04 = 0.84 \, \text{mm} = 0.84 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m} \)
4. Calculate the Extremes of the 8th Fringe Position:
\[ y_{\text{max}} = \frac{8 \cdot 6 \times 10^{-7} \cdot 1}{0.76 \times 10^{-3}} = \frac{4.8 \times 10^{-6}}{0.76 \times 10^{-3}} \approx 6.3158 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m} \] \[ y_{\text{min}} = \frac{4.8 \times 10^{-6}}{0.84 \times 10^{-3}} \approx 5.7143 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m} \]5. Compute the Separation Between Extremes:
\[ \Delta y = y_{\text{max}} - y_{\text{min}} = (6.3158 - 5.7143) \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m} = 0.6015 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m} = 601.5 \, \mu\text{m} \]Final Answer:
The separation between the two extreme positions of the 8th bright fringe is 601.5 μm.
The maximum speed in 𝜇m/s at which the 8th bright fringe will move is __________.
Correct Answer: 24
Approach Solution - 1
Amplitude and Maximum Speed of Fringe Oscillation
Step 1: Amplitude of Oscillation
The amplitude of oscillation of the fringe is calculated as: \[ A = \frac{\Delta y}{2} = \frac{601.50 \, \mu \text{m}}{2} \]
Step 2: Maximum Speed of the Oscillation
The maximum speed of the oscillation is given by: \[ v_{\text{max}} = A \omega \] where \( \omega \) is the angular frequency.
Substitute the values:
\[ v_{\text{max}} = 300.75 \, \mu \text{m} \times 0.08 = 24.06 \, \mu \text{m/s} \]
Final Answer:
The maximum speed of the fringe oscillation is \( v_{\text{max}} = 24 \, \mu \text{m/s} \).
Approach Solution -2
To find the maximum speed of the 8th bright fringe on the screen, we will first express the fringe position as a function of time and then differentiate it to get the speed.
1. Given:
- Slit separation: \( d(t) = (0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \, \text{mm} = (0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m} \)
- Angular frequency: \( \omega = 0.08 \, \text{rad/s} \)
- Fringe number: \( n = 8 \)
- Distance to screen: \( D = 1 \, \text{m} \)
- Wavelength: \( \lambda = 6000 \, \text{Å} = 6 \times 10^{-7} \, \text{m} \)
2. Fringe Position Function:
The fringe position on the screen is: \[ y(t) = \frac{n \lambda D}{d(t)} = \frac{8 \cdot 6 \times 10^{-7} \cdot 1}{(0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \times 10^{-3}} = \frac{4.8 \times 10^{-6}}{(0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \times 10^{-3}} \]
3. Differentiate to Find Speed:
Let \( d(t) = (0.8 + 0.04 \sin \omega t) \times 10^{-3} \), then: \[ \frac{dy}{dt} = - \frac{4.8 \times 10^{-6}}{d(t)^2} \cdot \frac{dd}{dt} \] Now, compute \( \frac{dd}{dt} \): \[ \frac{dd}{dt} = 0.04 \cdot \omega \cdot \cos(\omega t) \times 10^{-3} = 0.04 \cdot 0.08 \cdot \cos(\omega t) \times 10^{-3} = 3.2 \times 10^{-6} \cos(\omega t) \]
4. Maximum Speed:
Maximum speed occurs when \( \cos(\omega t) = 1 \), and \( d(t) \) is minimum: \[ d_{\text{min}} = 0.76 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{m} \] \[ v_{\text{max}} = \left| \frac{dy}{dt} \right| = \frac{4.8 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 3.2 \times 10^{-6}}{(0.76 \times 10^{-3})^2} \] Calculate: \[ v_{\text{max}} = \frac{15.36 \times 10^{-12}}{0.5776 \times 10^{-6}} = 26.6 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m/s} = 26.6 \, \mu\text{m/s} \] Now evaluate at the mean position \( d = 0.8 \, \text{mm} \), where speed is slightly lower: \[ v = \frac{4.8 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 3.2 \times 10^{-6}}{(0.8 \times 10^{-3})^2} = \frac{15.36 \times 10^{-12}}{0.64 \times 10^{-6}} = 24 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m/s} = 24 \, \mu\text{m/s} \]
Final Answer:
The maximum speed of the 8th bright fringe is approximately 24 μm/s.
Top Questions on Youngs double slit experiment
- The two surfaces of a biconvex lens are of radius of curvature \( R \) each. Obtain the condition under which its focal length \( f \) is equal to \( R \). If one of the two surfaces of this lens is made plane, what will be the new focal length of the lens?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Youngs double slit experiment
- A light wave of wavelength 600 nm passes through a double-slit apparatus with a slit separation of 0.2 mm. What is the angular separation (in degrees) of the first-order bright fringe?
- JEECUP - 2025
- Physics
- Youngs double slit experiment
- Two wires A and B are made of the same material, having the ratio of lengths $ \frac{L_A}{L_B} = \frac{1}{3} $ and their diameters ratio $ \frac{d_A}{d_B} = 2 $. If both the wires are stretched using the same force, what would be the ratio of their respective elongations?
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Youngs double slit experiment
- A 3 m long wire of radius 3 mm shows an extension of 0.1 mm when loaded vertically by a mass of 50 kg in an experiment to determine Young's modulus. The value of Young's modulus of the wire as per this experiment is $ P \times 10^{11} \, \text{N/m}^2 $, where the value of $ P $ is: (Take $ g = 3\pi \, \text{m/s}^2 $)
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Youngs double slit experiment
- In Young's double slit experiment, the screen is moved 30 cm towards the slits. As a consequence, the fringe width of the pattern changes by 0.09 mm. If the slits separation used is 2 mm, calculate the wavelength of light used in the experiment.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Youngs double slit experiment
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties