$Cu_2Cl_2$ and $CuCl_2$ in aqueous medium
- $CuCl_2$ is more stable than $Cu_2Cl_2$
- Stability of $Cu_2Cl_2$ is equal to stability of $CuCl_2$
- Both are unstable
- $Cu_2Cl_2$ is more stable than $CuCl_2$
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
In aqueous solutions, copper(I) chloride (Cu\(_2\)Cl\(_2\)) is more stable than copper(II) chloride (CuCl\(_2\)) due to the nature of copper ions and their oxidation states. Copper(I) chloride, in the form of Cu\(_2\)Cl\(_2\), is relatively stable because it tends to remain in the +1 oxidation state, whereas CuCl\(_2\), which contains copper in the +2 oxidation state, is less stable in aqueous medium due to the instability of copper(II) ions in water.
Thus, Cu\(_2\)Cl\(_2\) is more stable than CuCl\(_2\) in aqueous medium.
Approach Solution -2
Approach Solution -3
Cu$_2$Cl$_2$ is copper(I) chloride, which contains copper in the +1 oxidation state (Cu$^+$). In contrast, CuCl$_2$ is copper(II) chloride, where copper is in the +2 oxidation state (Cu$^{2+}$). The +1 oxidation state (Cu$^+$) is generally more stable in aqueous solutions compared to the +2 oxidation state (Cu$^{2+}$), because Cu$^{2+}$ is highly reactive and tends to get reduced to Cu$^+$. Therefore, Cu$_2$Cl$_2$ (copper(I) chloride) is more stable in aqueous medium than CuCl$_2$ (copper(II) chloride).
In an aqueous environment, copper(I) chloride (Cu$_2$Cl$_2$) is relatively stable as Cu$^+$ does not easily undergo oxidation to Cu$^{2+}$ in the presence of water. On the other hand, CuCl$_2$ (Cu$^{2+}$) is more prone to hydrolysis and reduction, making it less stable.
CuCl$_2$ is more likely to undergo reduction to Cu$_2$Cl$_2$ in aqueous solutions, especially under reducing conditions, which further demonstrates the greater stability of Cu$_2$Cl$_2$ compared to CuCl$_2$.
Thus, the correct answer is (A) Cu$_2$Cl$_2$ is more stable than CuCl$_2$.
Top Questions on Group 16 Elements
- Why does oxygen show anomalous behavior ?
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Group 16 Elements
- Choose the correct statements from the following:
A. All group 16 elements form oxides of general formula \( EO_2 \) and \( EO_3 \) where \( E = S, Se, Te, \) and Po. Both the types of oxides are acidic in nature.
B. TeO\(_2\) is an oxidising agent while SO\(_2\) is reducing in nature.
C. The reducing property decreases from H\(_2\)S to H\(_2\)Te down the group.
D. The ozone molecule contains five lone pairs of electrons.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Group 16 Elements
- From the given list, the number of compounds with +4 oxidation state of Sulphur_____.
\(SO_3, H_2SO_3, SOCl_2, SF_4, BaSO_4, H_2S_2O_7\).- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Group 16 Elements
- Among Group 16 elements, which one does NOT show -2 oxidation state?
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Group 16 Elements
- Given below are two statements :
Statement I: The boiling point of hydrides of Group 16 elements follow the order
H2O > H2Te > H2Se > H2S.
Statement II: On the basis of molecular mass, H2O is expected to have lower boiling point than the other members of the group but due to the presence of extensive H-bonding in H2O, it has higher boiling point.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Group 16 Elements
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives
Concepts Used:
Group 16 Elements
The group 16 elements (oxygen group elements) of the periodic classification are also known as chalcogens because most of the copper ores have copper in the form of oxides and sulphides. The word chalcogen means “ore formation” which is derived from the Greek word “Chalcos” (Ore) and “gen” (formation).
There are 5 elements that come under Group 16 of the Modern Periodic Table namely:
- Oxygen (O)
- Sulphur (S)
- Selenium (Se)
- Tellurium (Te)
- Polonium (PO)
Electronic Configuration:
The general electronic configuration of the chalcogens can be written as ‘ns2np4’, where ‘n’ denotes the value of the principal quantum number corresponding to the valence shell of the element.
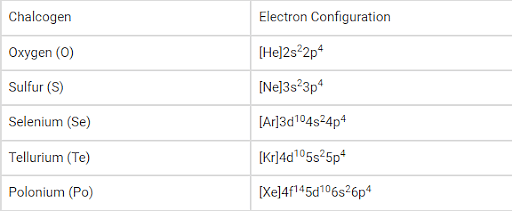
The electron configuration of the synthetic element livermorium (believed to be a chalcogen) is predicted to be [Rn]5f146d107s27p4.
Metallic Nature of the Group 16 Elements:
- Oxygen and sulfur are classified as non-metals.
- Selenium and tellurium are classified as metalloids.
- Under standard conditions, polonium exhibits metallic characteristics. However, it is important to note that polonium is a radioactive element.