Citrus canker is caused by
- mycoplasma
- virus
- fungus
- bacteria
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
Approach Solution -2
Citrus canker is caused by bacteria that belong to the genus Xanthomonas. It is a plant disease and is highly contagious. The plants that are affected by these bacteria will show symptoms of lesions on their leaves, stem and the fruits. This will eventually lead to the reduction in the yield of crops. The lesions have a water soaked area surrounding them that will give a ring-like appearance.
The spread of citrus canker can be attributed to wind driven rain or splashing water that have bacterial contamination.Even the tools and other equipment can be contaminated. The contamination of bacteria should be measured and controlled so that there is no reduction in the production and cultivation of the crops.
Learn with videos:
Top Questions on biological classification
- Which of the following microorganisms is used in the production of curd from milk?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- In a DNA molecule, which of the following base-pairings is correct?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- Which is not a prime element?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- Study the following and choose the incorrect combinations:
I. Phylum: Porifera, Special cells: Lasso cells, Example: Spongilla
II. Phylum: Cnidaria, Special cells: Stinging cells, Example: Hydra
III. Phylum: Ctenophora, Special cells: Choanocytes, Example: Pleurobrachia
IV. Phylum: Platyhelminthes, Special cells: Flame cells, Example: Fasciola- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- biological classification
- Study the following and choose the correct combinations:

- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- biological classification
Questions Asked in AIIMS exam
- The element Neodymium (Nd) belongs to the 4f series. What is its atomic number?
- AIIMS - 2024
- Modern Periodic Law And The Present Form Of The Periodic Table
- The correct increasing order of energy of orbitals in a hydrogen atom is:
- AIIMS - 2024
- Atomic Structure
- Which of the following is a globular protein?
- AIIMS - 2024
- Biomolecules
- Given that the surface charge density on a sphere is 200 μC/m2, what is the electric field at the surface of the sphere?
- AIIMS - 2024
- Electrostatics
- Which of the following is a crystalline solid?
- AIIMS - 2024
- The solid state
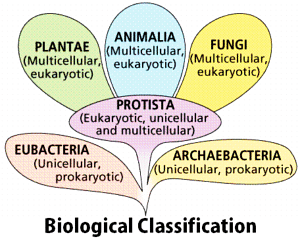
Concepts Used:
Biological Classification
The process of grouping living organisms into categories is called biological classification. The most modern 5-kingdom classification was put ahead by an eminent scientist R.H.Whittaker. The five-kingdom classification is based on the criteria like cell structure, mode of nutrition, body form, and reproduction. One of the most important characteristics of this system is that it follows the evolutionary sequence of living organisms. The organisms are classified into distinct taxa or levels like Kingdom, Phylum, Division, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. The 5 kingdoms are as follows: