According to MO theory, number of species/ions from the following having identical bond order is ___.
CN-, NO+, O2, O+2, O2+2
CN-, NO+, O2, O+2, O2+2
Correct Answer: 3
Approach Solution - 1
To find the number of species/ions with an identical bond order using Molecular Orbital (MO) theory, we need to calculate the bond order for each given species using the formula: Bond Order = (Number of bonding electrons - Number of antibonding electrons) / 2.
- CN-:
The electronic configuration is (σ1s)2(σ1s*)2(σ2s)2(σ2s*)2(π2p)4(σ2p)2.
Bonding electrons: 10, Antibonding electrons: 4.
Bond Order = (10 - 4) / 2 = 3. - NO+:
The electronic configuration is (σ1s)2(σ1s*)2(σ2s)2(σ2s*)2(π2p)4(σ2p)2.
Bonding electrons: 10, Antibonding electrons: 4.
Bond Order = (10 - 4) / 2 = 3. - O2:
The electronic configuration is (σ1s)2(σ1s*)2(σ2s)2(σ2s*)2(π2p)4(π2p*)2.
Bonding electrons: 10, Antibonding electrons: 6.
Bond Order = (10 - 6) / 2 = 2. - O2+:
The electronic configuration is (σ1s)2(σ1s*)2(σ2s)2(σ2s*)2(π2p)4(π2p*)1.
Bonding electrons: 10, Antibonding electrons: 5.
Bond Order = (10 - 5) / 2 = 2.5. - O22+:
The electronic configuration is (σ1s)2(σ1s*)2(σ2s)2(σ2s*)2(π2p)4.
Bonding electrons: 10, Antibonding electrons: 4.
Bond Order = (10 - 4) / 2 = 3.
Species with identical bond order of 3: CN-, NO+, O22+.
Number of such species = 3, which fits within the provided range (3,3).
Approach Solution -2
CN-, NO+ and \(O_2^{2+} \)have bond order of `3'.
O2 has bond order of 2,
\(O_2^+\) has bond order of 2.5.
∴ Three species have similar bond order.
Top Questions on Ammonia
- When a salt is treated with sodium hydroxide solution, it gives gas X. On passing gas X through reagent Y, a brown coloured precipitate is formed. X and Y respectively, are:
- A gas ‘X’ is added to Nessler’s reagent then brown precipitate is formed, gas X is
- Ammonia is synthesized in the Haber process in the following reaction.
$𝑁_2 (𝑔) + 3𝐻_2 (𝑔) → 2𝑁𝐻_3(𝑔)$
The temperature above which the reaction becomes spontaneous is __________ 𝐾 (rounded off to one decimal place).
($\bigtriangleup 𝐻^0 = −92.2 𝑘𝐽, \bigtriangleup 𝑆^0 = −199 𝐽𝐾^{ −1}$ ) - The dehydrating agent for ammonia used in laboratory is
- Reaction of [Co(H2O)6]2+ with excess ammonia and in the presence of oxygen results into a diamagnetic product. Number of electrons present in t2g-orbitals of the product is _______
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- In a microscope of tube length $10\,\text{cm}$ two convex lenses are arranged with focal lengths $2\,\text{cm}$ and $5\,\text{cm}$. Total magnification obtained with this system for normal adjustment is $(5)^k$. The value of $k$ is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Optical Instruments
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
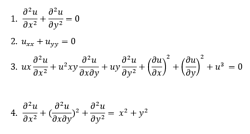
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
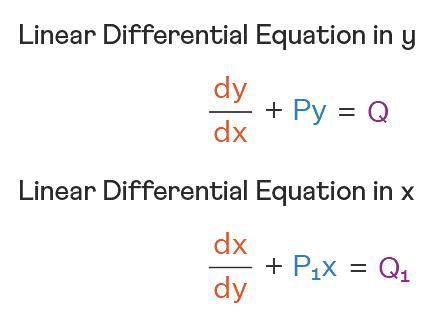
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations