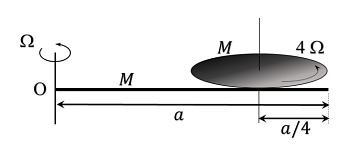
A thin rod of mass $M$ and length $a$ is free to rotate in horizontal plane about a fixed vertical axis passing through point $O$. A thin circular disc of mass $M$ and of radius $a / 4$ is pivoted on this rod with its center at a distance $a / 4$ from the free end so that it can rotate freely about its vertical axis, as shown in the figure. Assume that both the rod and the disc have uniform density and they remain horizontal during the motion. An outside stationary observer finds the rod rotating with an angular velocity $\Omega$ and the disc rotating about its vertical axis with angular velocity $4\, \Omega$. The total angular momentum of the system about the point $O$ is $\left(\frac{ Ma ^{2} \Omega}{48}\right) n$. The value of $n$ is ______

Correct Answer: 49
Solution and Explanation
Given:
- Thin rod of mass M and length a rotating about point O with angular velocity Ω
- A thin disc of mass M and radius a/4 is attached at distance a/4 from the free end of the rod
- The disc is rotating with angular velocity 4Ω about its own vertical axis
- We are to find the total angular momentum of the system about point O in terms of (M a² Ω / 48)·n
Step 1: Angular momentum of the rod about point O
Moment of inertia of thin rod about one end (axis perpendicular to length):
Irod = (1/3) M a²
Angular momentum = I × Ω = (1/3) M a² Ω
Step 2: Angular momentum of the disc
Total angular momentum of the disc has two parts:
- Due to rotation of the disc's center about O:
- Due to spinning of the disc about its own axis:
Total disc angular momentum = (9/16 + 1/8) M a² Ω
Convert to common denominator: (9/16 + 2/16) = 11/16
So, Ldisc = (11/16) M a² Ω
Step 3: Total angular momentum about O
Ltotal = Lrod + Ldisc = (1/3) M a² Ω + (11/16) M a² Ω
Take LCM:
(1/3) = (16/48), (11/16) = (33/48)
⇒ Ltotal = (16 + 33)/48 M a² Ω = (49/48) M a² Ω
Final Answer: n = 49
Top Questions on Rotational motion
Two circular discs of radius \(10\) cm each are joined at their centres by a rod, as shown in the figure. The length of the rod is \(30\) cm and its mass is \(600\) g. The mass of each disc is also \(600\) g. If the applied torque between the two discs is \(43\times10^{-7}\) dyne·cm, then the angular acceleration of the system about the given axis \(AB\) is ________ rad s\(^{-2}\).

- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Rotational motion
Two point charges 2q and q are placed at vertex A and centre of face CDEF of the cube as shown in figure. The electric flux passing through the cube is :

- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Rotational motion
- A solid sphere of radius \(10\) cm is rotating about an axis which is at a distance \(15\) cm from its centre. The radius of gyration about this axis is \( \sqrt{n} \) cm. Find the value of \( n \).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Rotational motion
- A simple pendulum made of mass 10 g and a metallic wire of length 10 cm is suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field of 2 T. The magnetic field direction is perpendicular to the plane of oscillations of the pendulum. If the pendulum is released from an angle of 60° with vertical, then maximum induced EMF between the point of suspension and point of oscillation is_______ mV. (Take g = 10 m/s²)}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Rotational motion
Suppose there is a uniform circular disc of mass M kg and radius r m shown in figure. The shaded regions are cut out from the disc. The moment of inertia of the remainder about the axis A of the disc is given by $\frac{x{256} Mr^2$. The value of x is ___.

- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Rotational motion
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
Rotational Motion
Rotational motion can be defined as the motion of an object around a circular path, in a fixed orbit.
Rotational Motion Examples:
The wheel or rotor of a motor, which appears in rotation motion problems, is a common example of the rotational motion of a rigid body.
Other examples:
- Moving by Bus
- Sailing of Boat
- Dog walking
- A person shaking the plant.
- A stone falls straight at the surface of the earth.
- Movement of a coin over a carrom board
Types of Motion involving Rotation:
- Rotation about a fixed axis (Pure rotation)
- Rotation about an axis of rotation (Combined translational and rotational motion)
- Rotation about an axis in the rotation (rotating axis)