A stationary source (see figure) emits sound waves of frequency $f$ towards a stationary wall.
If an observer moving with speed u in a direction perpendicular to the wall measures a frequency $f' = \frac{11}{8} f $ at the instant shown, then $u$ is related to the speed of sound $V_S$ as
- $\frac{3}{4} Vs$
- $\frac{3}{8} Vs$
- $\frac{1}{4} Vs$
- $\frac{8}{3} Vs$
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
When energy leaves a sound source, it causes patterns of disturbances called sound waves. Sound is the vibration that travels through a material like a gas, liquid, or solid as an audible wave of pressure.
A sound is a type of wave that travels through a medium at various frequencies until it reaches our ears and is audible to us. A sound is a type of vibration that travels through a medium as mechanical waves. Solid, liquid, and gaseous media all allow for the propagation of sound waves. Compared to liquid and gaseous media, the solid medium allows sound waves to move more quickly.
Sound waves can be defined as The patterns of disturbances that are caused by the movement of energy travelling via a medium

- It is a technique for moving energy in the form of longitudinal mechanical waves from one location to another.
- Sound waves cannot travel in a vacuum and need a medium to do so.
- When a disturbance occurs in a medium, sound waves are created, and sound waves move longitudinally, which means that the vibration of the particles is parallel to the direction of the transmission of the energy wave.
- A zone of high and low pressure is created in the medium as a result of the particle motion.
- Compression and rarefaction are terms used to describe the high-pressure and low-pressure zones, respectively.
These areas transfer to a different medium, which is also responsible for the sound's transmission there.
Some important terms and formulae related to sound waves are mentioned below:
- Period: The time required to complete the one cycle by sound waves, is denoted by T.
- Frequency: It is the number of cycles completed by sound waves in one second, denoted by nu(v). Formula: Frequency = 1/T
- Wavelength (λ): It is the distance covered between two compressions and the rarefaction of sound waves. Formula: Wavelength (λ) = v/F
- Amplitude: It is the maximum distance traveled by the particle on either side of the compression and interaction of the sound waves
Top Questions on doppler effect
- A passenger is sitting in a fast moving train. The engine of the train blows a whistle of frequency N. If the apparent frequency of sound heard by the passengers is \( N' \), then:
- MHT CET - 2025
- Physics
- doppler effect
- When both the source of sound and observer approach each other with a speed equal to 10% of the speed of sound, then the percentage change in frequency heard by the observer is nearly
- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Physics
- doppler effect
- A source (S) of sound has frequency\( 240 Hz\). When the observer (O) and the source move towards each other at a speed \(v\) with respect to the ground (as shown in Case 1 in the figure), the observer measures the frequency of the sound to be \(288 Hz\). However, when the observer and the source move away from each other at the same speed v with respect to the ground (as shown in Case 2 in the figure), the observer measures the frequency of sound to be \(n\) Hz. The value of \(n\) is _____.
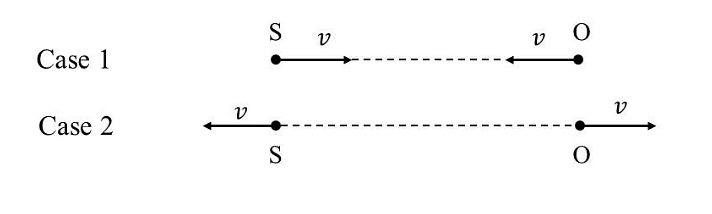
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- doppler effect
- A galaxy is moving away from the Earth so that a spectral line at 6000 Å is observed at 6300 Å. Then the speed of the galaxy with respect to the Earth is
- KCET - 2024
- Physics
- doppler effect
- A train is moving with a speed of \(10 m/s\) towards a platform and blows a horn with frequency \(400 Hz\). Find the frequency heard by a passenger standing on the platform. Take speed of sound = \(310 m/s\).
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- doppler effect
Questions Asked in UPSEE exam
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose
- UPSEE - 2019
- Carbohydrates
- The imaginary part of $\left( \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{2}i\right)^{10} $ is
- UPSEE - 2019
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Acetic acid dissociates 1.3%. What will be the pH of \(\frac {N}{10}\) solution of the acid.
- UPSEE - 2019
- Acids and Bases
Let z = x + iy be a complex number satisfying the following equation |z - (2 + i)| = |Re(z) - 4 | Which of the following options describes the above equation?
- UPSEE - 2019
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Let $a_1, a_2, a_3$, ... be an arithmetic progression with nonzero common difference. It is given that $\sum^{12}_{i = 4} a_i = 63$ and $a_k = 7 $ for some k . Then the value of k is
- UPSEE - 2019
- Arithmetic Progression
Concepts Used:
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect is a phenomenon caused by a moving wave source that causes an apparent upward shift in frequency for observers who are approaching the source and a visible downward change in frequency for observers who are retreating from the source. It's crucial to note that the impact isn't caused by a change in the source's frequency.

The Doppler effect may be seen in any wave type, including water waves, sound waves, and light waves. We are most familiar with the Doppler effect because of our encounters with sound waves
