A letter lock consists of three rings with 15 different letters. If N denotes the number of ways in which it is possible to make unsuccessful attempts to open the lock, Then
- 482 divides N
- N is the product of two distinct prime numbers.
- N is the product of three distinct prime numbers.
- 16 divides N
The Correct Option is A, C
Approach Solution - 1
Total possible combinations: Each ring has 15 letters: \[ 15 \times 15 \times 15 = 3375 \] Number of unsuccessful attempts: \[ N = 3375 - 1 = 3374 \] Check (A): Does 482 divide N? Check if: \[ 3374 \div 482 = 7 \Rightarrow 3374 = 482 \times 7 \Rightarrow \text{Yes, 482 divides } N \] Check (C): Is N the product of 3 distinct prime numbers? Prime factorization of 3374: \[ 3374 = 2 \times 1687 \] Factor 1687: \[ 1687 = 19 \times 89 \Rightarrow 3374 = 2 \times 19 \times 89 \] All are distinct primes, so yes.
Correct options: (A) ✅ 482 divides N (C) ✅ N is the product of three distinct primes
Approach Solution -2
Total permutations: Each digit can be chosen in 15 ways (say, from a set of 15 symbols). So, the total number of possible 3-digit patterns: \[ 15 \times 15 \times 15 = 3375 \] Unsuccessful attempts: Only one is the correct pattern, so: \[ 3375 - 1 = 3374 \] Now factorize 3374: \[ 3374 = 2 \times 7 \times 241 \] Hence: Let \(N = 3374\), then: - Option (A)(C) Correct options: (A) ✅ (C) ✅
Top Questions on Straight lines
- Rhombus vertices A(1,2), C(-3,-6). Line AD parallel to $7x-y=14$. Find $|\alpha+\beta+\gamma+\delta|$.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- Let the angles made with the positive $x$-axis by two straight lines drawn from the point $P(2,3)$ and meeting the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$ from the point $P$ be $\theta_1$ and $\theta_2$. Then the value of $(\theta_1+\theta_2)$ is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- If two lines drawn from a point $P(2,3)$ intersect the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}$, then the angle between the lines is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- If two lines drawn from a point $P(2,3)$ intersect the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}$, then the angle between the lines is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- The equation of a straight line is given by \( y = 3x + 4 \). What is the slope of the line?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
Questions Asked in WBJEE exam
- Figure shows the graph of angle of deviation \( \delta \) versus angle of incidence \( i \) for a light ray striking a prism. The prism angle is

- WBJEE - 2025
- Refraction Through A Prism
- Ruma reached the metro station and found that the escalator was not working. She walked up the stationary escalator with velocity \( v_1 \) in time \( t_1 \). On another day, if she remains stationary on the escalator moving with velocity \( v_2 \), the escalator takes her up in time \( t_2 \). The time taken by her to walk up with velocity \( v_1 \) on the moving escalator will be:
- WBJEE - 2025
- Relative Motion
- The compound(s) showing optical activity is/are
- WBJEE - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about the given compound?

- WBJEE - 2025
- Organic Chemistry
- X is an extensive property and x is an intensive property of a thermodynamic system. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
- WBJEE - 2025
- Thermodynamics
Concepts Used:
Straight lines
A straight line is a line having the shortest distance between two points.
A straight line can be represented as an equation in various forms, as show in the image below:
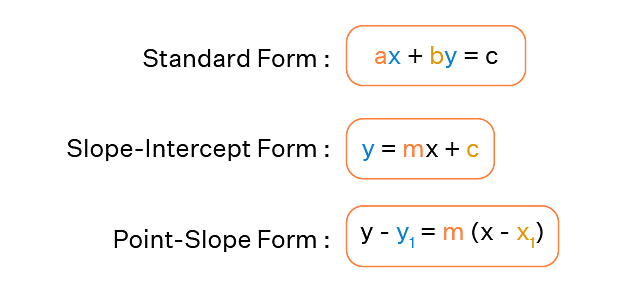
The following are the many forms of the equation of the line that are presented in straight line-
1. Slope – Point Form
Assume P0(x0, y0) is a fixed point on a non-vertical line L with m as its slope. If P (x, y) is an arbitrary point on L, then the point (x, y) lies on the line with slope m through the fixed point (x0, y0) if and only if its coordinates fulfil the equation below.
y – y0 = m (x – x0)
2. Two – Point Form
Let's look at the line. L crosses between two places. P1(x1, y1) and P2(x2, y2) are general points on L, while P (x, y) is a general point on L. As a result, the three points P1, P2, and P are collinear, and it becomes
The slope of P2P = The slope of P1P2 , i.e.
\(\frac{y-y_1}{x-x_1} = \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}\)
Hence, the equation becomes:
y - y1 =\( \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1} (x-x1)\)
3. Slope-Intercept Form
Assume that a line L with slope m intersects the y-axis at a distance c from the origin, and that the distance c is referred to as the line L's y-intercept. As a result, the coordinates of the spot on the y-axis where the line intersects are (0, c). As a result, the slope of the line L is m, and it passes through a fixed point (0, c). The equation of the line L thus obtained from the slope – point form is given by
y – c =m( x - 0 )
As a result, the point (x, y) on the line with slope m and y-intercept c lies on the line, if and only if
y = m x +c