Integrate the rational function: \(\frac {5x}{(x+1)(x^2-4)}\)
Solution and Explanation
\(\frac {5x}{(x+1)(x^2-4)}\)= \(\frac {5x}{(x+1)(x+2)(x-2)}\)
Let \(\frac {5x}{(x+1)(x+2)(x-2)}\) = \(\frac {A}{(x+1)} +\frac {B}{(x+2)} + \frac {C}{(x-2)}\)
\(5x = A(x+2)(x-2) + B(x+1)(x-2) + C(x+1)(x+2) ….....(1)\)
Substituting x = −1, −2, and 2 respectively in equation (1), we obtain
A = \(\frac 53\), B= \(-\frac {5}{2}\), and C = \(\frac 56\)
∴ \(\frac {5x}{(x+1)(x+2)(x-2)}\) = \(\frac {5}{3(x+1)} -\frac {5}{2(x+2)} + \frac {5}{6(x-2)}\)
⇒ \(∫\)\(\frac {5x}{(x+1)(x+2)(x-2)} \ dx\) = \(\frac 53 ∫\frac {1}{(x+1)}dx-\frac 52 ∫\frac {1}{(x+2)}dx+\frac 56 ∫\frac {1}{(x-2)}dx\)
= \(\frac 53\ log|x+1|-\frac 52\ log|x+2|+\frac 56\ log|x-2|+C\)
Top Questions on integral
Let \( f : (0, \infty) \to \mathbb{R} \) be a twice differentiable function. If for some \( a \neq 0 \), } \[ \int_0^a f(x) \, dx = f(a), \quad f(1) = 1, \quad f(16) = \frac{1}{8}, \quad \text{then } 16 - f^{-1}\left( \frac{1}{16} \right) \text{ is equal to:}\]
- Let $ f(x) $ be a positive function and $I_1 = \int_{-\frac{1}{2}}^1 2x \, f\left(2x(1-2x)\right) dx$ and $I_2 = \int_{-1}^2 f\left(x(1-x)\right) dx.$ Then the value of $\frac{I_2}{I_1}$ is equal to ____
- Evaluate the integral: \[ \int \frac{x^2 + 2x}{\sqrt{x^2 + 1}} \, dx \]
- Evaluate the integral: \[ \int \sqrt{x^2 + 3x} \, dx \]
- The value of the integral \( \int_0^1 x^2 \, dx \) is:
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
If vector \( \mathbf{a} = 3 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} - \hat{k} \) \text{ and } \( \mathbf{b} = \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} \), then which of the following is correct?
- Find the value of $x$, if \[ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 & 2 \\ 2 & 5 & 1 \\ 15 & 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ x \\ 2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \]
- Two point charges of \( -5\,\mu C \) and \( 2\,\mu C \) are located in free space at \( (-4\,\text{cm}, 0) \) and \( (6\,\text{cm}, 0) \) respectively.
(a) Calculate the amount of work done to separate the two charges at infinite distance.
(b) If this system of charges was initially kept in an electric field \[ \vec{E} = \frac{A}{r^2}, \text{ where } A = 8 \times 10^4\, \text{N}\,\text{C}^{-1}\,\text{m}^2, \] calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the system.- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Electrostatics
- 4,000 shares of ₹ 10 each were forfeited for non-payment of second and final call money of ₹ 2 per share. The minimum amount that the company must collect at the time of reissue of these shares will be :
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Accounting for Share Capital
- If $y = a \cos(\log x) + b \sin(\log x)$, then $x^2y'' + xy'1$ is:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Continuity and differentiability
Concepts Used:
Integration by Partial Fractions
The number of formulas used to decompose the given improper rational functions is given below. By using the given expressions, we can quickly write the integrand as a sum of proper rational functions.
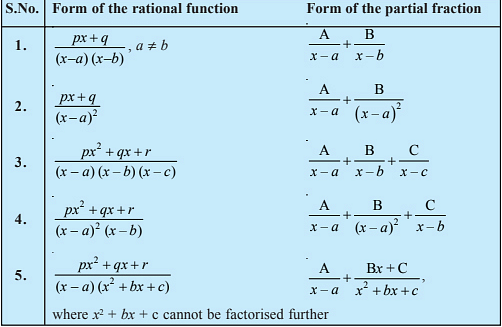
For examples,
