Integrate the rational function: \(\frac{2x-3}{(x^2-1)(2x+3)}\)
Solution and Explanation
\(\frac{2x-3}{(x^2-1)(2x+3)}\)= \(\frac{2x-3}{(x+1)(x-1)(2x+3)}\)
Let \(\frac{2x-3}{(x+1)(x-1)(2x+3)}= \frac{A}{(x+1)}\frac{B}{(x-1)}+\frac{C}{(2x+3)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) (2x-3) = A(x-1)(2x+3)+B(x+1)(2x+3)+C(x+1)(x-1)
\(\Rightarrow\) (2x-3) = A(2x2+x-3)+B(2x2+5x+3)+C(x2-1)
\(\Rightarrow\) (2x-3) = A(2A+2B+C)x2+(A+5B)x+(-3A+3B-C)
Equating the coefficients of x2 and x, we obtain
B = -\(\frac{1}{10}\), A = \(\frac{5}{2}\), and C = -\(\frac{24}{5}\)
∴ \(\frac{2x-3}{(x+1)(x-1)(2x+3)}= \frac{5}{2(x+1)}\frac{1}{10(x-1)}+\frac{24}{5(2x+3)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\int\frac{2x-3}{(x+1)(x-1)(2x+3)}dx= \frac{5}{2}\int\frac{1}{(x+1)}dx-\frac{1}{10}\int\frac{1}{x-1}dx-\frac{24}{5}\int\frac{1}{(2x+3)}dx\)
= \(\frac{5}{2}\log\mid x+1\mid-\frac{1}{10}\log \mid x-1\mid-\frac{24}{5*2}\log\mid 2x+3\mid\)
=\(\frac{5}{2}\log\mid x+1\mid-\frac{1}{10}\log\mid x-1\mid-\frac{12}{5}\log\mid 2x+3 \mid+C\)
Top Questions on integral
Let \( f : (0, \infty) \to \mathbb{R} \) be a twice differentiable function. If for some \( a \neq 0 \), } \[ \int_0^a f(x) \, dx = f(a), \quad f(1) = 1, \quad f(16) = \frac{1}{8}, \quad \text{then } 16 - f^{-1}\left( \frac{1}{16} \right) \text{ is equal to:}\]
- Let $ f(x) $ be a positive function and $I_1 = \int_{-\frac{1}{2}}^1 2x \, f\left(2x(1-2x)\right) dx$ and $I_2 = \int_{-1}^2 f\left(x(1-x)\right) dx.$ Then the value of $\frac{I_2}{I_1}$ is equal to ____
- Evaluate the integral: \[ \int \frac{x^2 + 2x}{\sqrt{x^2 + 1}} \, dx \]
- Evaluate the integral: \[ \int \sqrt{x^2 + 3x} \, dx \]
- The value of the integral \( \int_0^1 x^2 \, dx \) is:
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
- Suppose, the value of Average Propensity to Consume (APC) is 0.8 and National Income is ₹ 4,000 crores, the value of saving would be ₹ ____ crores. (Choose the correct option to fill up the blank)
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Income and Employment
- Surface area of a balloon (spherical), when air is blown into it, increases at a rate of 5 mm²/s. When the radius of the balloon is 8 mm, find the rate at which the volume of the balloon is increasing.
- Two wires of the same material and the same radius have their lengths in the ratio 2:3. They are connected in parallel to a battery which supplies a current of 15 A. Find the current through the wires.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Current electricity
- (a) Briefly explain Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
(b) Four metals with their work functions are listed below:
K = 2.3 eV, Na = 2.75 eV, Mo = 4.17 eV, Ni = 5.15 eV.
The radiation of wavelength 330 nm from a laser source placed 1 m away, falls on these metals.
Which of these metals will not show photoelectric emission?
What will happen if the laser source is brought closer to a distance of 50 cm?- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Photoelectric Effect
- Differentiate $2\cos^2 x$ w.r.t. $\cos^2 x$.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Derivatives
Concepts Used:
Integration by Partial Fractions
The number of formulas used to decompose the given improper rational functions is given below. By using the given expressions, we can quickly write the integrand as a sum of proper rational functions.
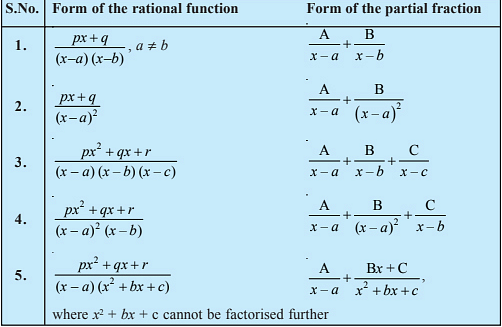
For examples,
