Question:
Which of the following statements is true about a chiral carbon?
Which of the following statements is true about a chiral carbon?
Show Hint
A chiral carbon is defined by its attachment to four different groups. This asymmetry leads to chirality, which is fundamental in stereochemistry.
Updated On: Apr 12, 2025
- A chiral carbon is attached to two identical groups.
- A chiral carbon must be attached to four different groups.
- A chiral carbon cannot exist in molecules with symmetry.
- A chiral carbon is always part of an alkene.
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
A chiral carbon is a carbon atom that is attached to four different groups. This gives rise to chirality, which results in non-superimposable mirror images, or enantiomers. A molecule with a chiral carbon is asymmetric and does not have symmetry.
- Option (A) is incorrect because a chiral carbon cannot be attached to two identical groups, as this would create a plane of symmetry, making the carbon achiral.
- Option (C) is incorrect because chiral carbons can exist in molecules with symmetry, as long as they are attached to four different groups.
- Option (D) is incorrect because a chiral carbon is not always part of an alkene; it can be part of many other types of molecules as well. Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
- Option (C) is incorrect because chiral carbons can exist in molecules with symmetry, as long as they are attached to four different groups.
- Option (D) is incorrect because a chiral carbon is not always part of an alkene; it can be part of many other types of molecules as well. Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Chirality & symmetry of organic molecules with or without chiral centres
- Which of the following molecules is chiral in nature?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Chirality & symmetry of organic molecules with or without chiral centres
- In the given molecule,

the number of chiral centers is _______.- IIT JAM BT - 2024
- Chemistry
- Chirality & symmetry of organic molecules with or without chiral centres
- The correct statement(s) about the relationship for the H-atoms in the following compounds is (are) :
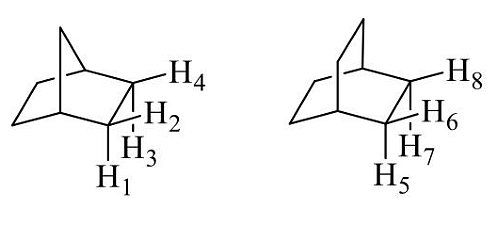
- GATE CY - 2024
- Organic Chemistry
- Chirality & symmetry of organic molecules with or without chiral centres
- Among the following, the chiral compound is
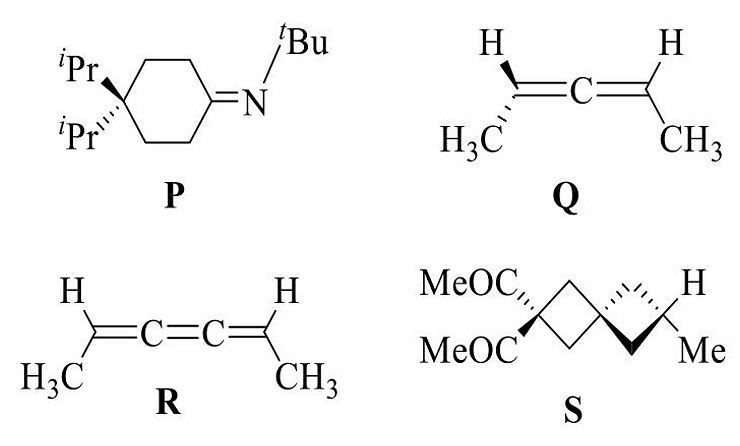
- GATE CY - 2024
- Organic Chemistry
- Chirality & symmetry of organic molecules with or without chiral centres
- An organic compound exhibits the [M]+, [M+2]+, and [M+4]+ peaks in the intensity ratio 1:2:1 in the mass spectrum, and shows a singlet at \( \delta \) 7.49 in the \( ^1H \) NMR spectrum in CDCl\(_3\). The compound is:
- GATE CY - 2021
- Organic Chemistry
- Chirality & symmetry of organic molecules with or without chiral centres
View More Questions
Questions Asked in MHT CET exam
Which part of root absorb mineral?
- MHT CET - 2025
- The Root
- A body of mass 2 kg is moving in a circular path of radius 3 m with a constant speed of 6 m/s. What is the centripetal force acting on the body?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Centripetal forces
- A 200 g sample of water at 80°C is mixed with 100 g of water at 20°C. Assuming no heat loss to the surroundings, what is the final temperature of the mixture?
- MHT CET - 2025
- thermal properties of matter
- Given the equation: \[ 81 \sin^2 x + 81 \cos^2 x = 30 \] Find the value of \( x \).
- MHT CET - 2025
- Trigonometric Identities
- A body of mass 10 kg is at a height of 5 m above the surface of the Earth. What is the gravitational potential energy of the body? (Take \( g = 10 \, \text{m/s}^2 \))
- MHT CET - 2025
- Gravitational Potential Energy
View More Questions