Which of the following have square pyramidal structure?
- XeOF4
- BrF3
- XeF4
- XeO3
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
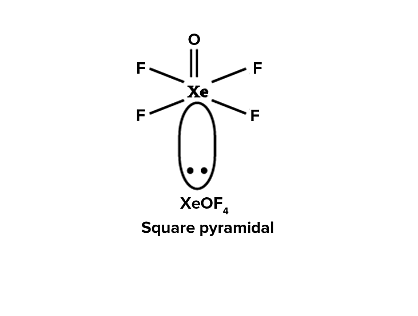
XeOF₄ and its Structure:
- Chemical Formula: XeOF₄ (Xenon oxytetrafluoride).
- Central Atom: Xenon (Xe).
- Electron Pair Arrangement:
- Xenon has 8 valence electrons.
- 4 fluorine atoms and 1 oxygen atom are bonded to Xenon.
- 1 lone pair remains on Xenon after bonding.
- Molecular Geometry: Square pyramidal (AX5E type) due to the presence of:
- 5 bonded groups (4 fluorine atoms + 1 oxygen atom).
- 1 lone pair, which distorts the structure into a square pyramidal shape.
Key Observations:
Due to the lone pair of electrons on Xe, the molecule adopts a square pyramidal geometry. This geometry is confirmed by VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory, where the lone pair repels the bonded atoms, causing this specific shape.
Conclusion:
The correct answer is: XeOF₄ has a square pyramidal structure.
Top Questions on Chemical bonding and molecular structure
From the given following (A to D) cyclic structures, those which will not react with Tollen's reagent are :

- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- The wave numbers of three spectral lines of hydrogen atom are considered. Identify the set of spectral lines belonging to the {Balmer series. (\(R\) = Rydberg constant)}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Consider the reaction: \[ \text{Ph–CH=CH}_2 \xrightarrow[\text{peroxide}]{\text{HBr}} \text{Product} \] Which of the following statements are correct?
[A.] The reaction proceeds through a more stable radical intermediate.
[B.] The role of peroxide is to generate \(\mathrm{H^\bullet}\) radical.
[C.] During this reaction, benzene is formed as a byproduct.
[D.] \(1\)-Bromo-\(2\)-phenylethane is formed as a minor product.
[E.] The same reaction in absence of peroxide proceeds via a carbocation intermediate. Choose the correct answer.- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Compound 'P' undergoes the following sequence of reactions : (i) NH₃ (ii) $\Delta$ $\rightarrow$ Q (i) KOH, Br₂ (ii) CHCl₃, KOH (alc), $\Delta$ $\rightarrow$ NC-CH₃. 'P' is :


- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Given below are two statements :
Statement I : The correct order in terms of bond dissociation enthalpy is \( Cl_2>Br_2>F_2>I_2 \).
Statement II : The correct trend in the covalent character of the metal halides is \( SnCl_2>SnCl_4 \), \( PbCl_2>PbCl_4 \) and \( UF_4>UF_6 \).
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Which one of the following graphs accurately represents the plot of partial pressure of CS₂ vs its mole fraction in a mixture of acetone and CS₂ at constant temperature?


- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
- Let \( ABC \) be an equilateral triangle with orthocenter at the origin and the side \( BC \) lying on the line \( x+2\sqrt{2}\,y=4 \). If the coordinates of the vertex \( A \) are \( (\alpha,\beta) \), then the greatest integer less than or equal to \( |\alpha+\sqrt{2}\beta| \) is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electromagnetic waves
Let \( \alpha = \dfrac{-1 + i\sqrt{3}}{2} \) and \( \beta = \dfrac{-1 - i\sqrt{3}}{2} \), where \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). If
\[ (7 - 7\alpha + 9\beta)^{20} + (9 + 7\alpha - 7\beta)^{20} + (-7 + 9\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} + (14 + 7\alpha + 7\beta)^{20} = m^{10}, \] then the value of \( m \) is ___________.- JEE Main - 2026
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- The work functions of two metals ($M_A$ and $M_B$) are in the 1 : 2 ratio. When these metals are exposed to photons of energy 6 eV, the kinetic energy of liberated electrons of $M_A$ : $M_B$ is in the ratio of 2.642 : 1. The work functions (in eV) of $M_A$ and $M_B$ are respectively.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Dual nature of matter
Concepts Used:
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Such a group of atoms is called a molecule. Obviously, there must be some force that holds these constituent atoms together in the molecules. The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together in different chemical species is called a chemical bond.
Types of Chemical Bonds:
There are 4 types of chemical bonds which are formed by atoms or molecules to yield compounds.
- Ionic Bonds - Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding which involves a transfer of electrons from one atom or molecule to another.
- Covalent Bonds - Compounds that contain carbon commonly exhibit this type of chemical bonding.
- Hydrogen Bonds - It is a type of polar covalent bonding between oxygen and hydrogen wherein the hydrogen develops a partial positive charge
- Polar Bonds - In Polar Covalent chemical bonding, electrons are shared unequally since the more electronegative atom pulls the electron pair closer to itself and away from the less electronegative atom.
Factors Affecting Bond Enthalpy in Chemical Bonding:
- Size of the Atom
- Multiplicity of Bonds
- Number of Lone Pair of Electrons Present
- Bond Angle