What causes poisoning of Carbon Monoxide?
Approach Solution - 1
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning occurs when an individual inhales or is exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide gas. Carbon monoxide is produced by the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels such as gasoline, natural gas, wood, coal, and propane. It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas, making it difficult to detect without specialized equipment.
The main cause of carbon monoxide poisoning is the inhalation of carbon monoxide gas. This gas binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, forming carboxyhemoglobin. Carboxyhemoglobin has a much stronger affinity for oxygen than regular hemoglobin, which prevents the transport of oxygen to body tissues. As a result, oxygen deprivation occurs, leading to cellular damage and potentially life-threatening conditions.
Common sources of carbon monoxide include:
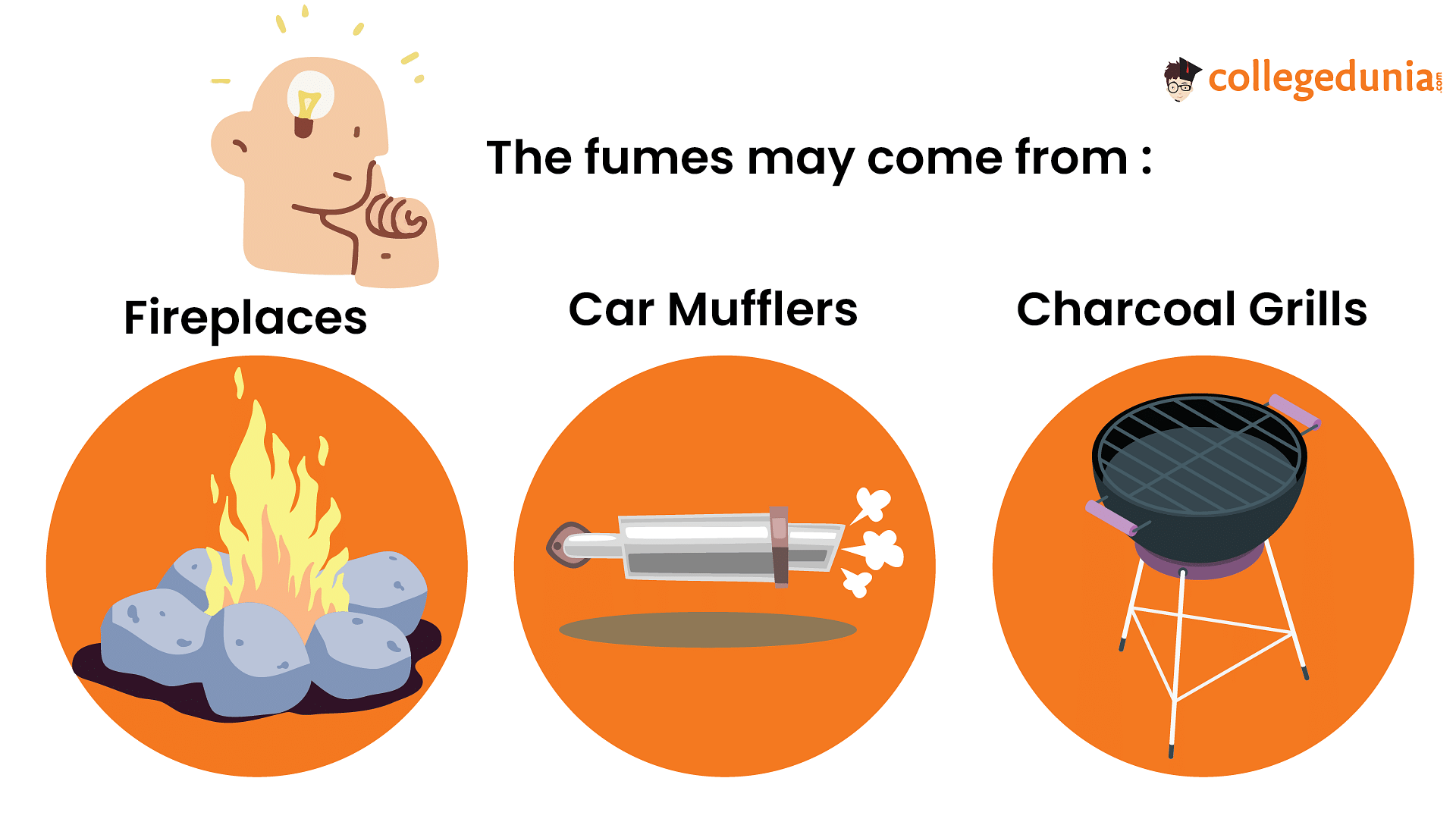
- Faulty or poorly maintained fuel-burning appliances: This includes malfunctioning furnaces, gas stoves, water heaters, fireplaces, and space heaters.
- Vehicle exhaust: Carbon monoxide can accumulate in enclosed spaces such as garages, tunnels, or poorly ventilated areas near running vehicles.
- Generators and power tools: Operating gasoline-powered generators or tools in enclosed spaces without proper ventilation can lead to carbon monoxide buildup.
- Tobacco smoke: Smoking or inhaling secondhand smoke exposes individuals to carbon monoxide, which can contribute to overall carbon monoxide levels in the body.
- Blocked chimneys or vents: Blockages in chimneys, flues, or vents can cause carbon monoxide to back up into living spaces instead of being properly vented outdoors.
The symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning can vary depending on the level and duration of exposure. Early symptoms often resemble flu-like symptoms, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and confusion. Prolonged exposure to high levels of carbon monoxide can lead to loss of consciousness, seizures, organ damage, and even death.
To prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, it is crucial to have fuel-burning appliances and heating systems inspected and maintained regularly. Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home, especially near sleeping areas. Ensure proper ventilation and avoid running vehicles or gas-powered equipment in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces. It is important to take immediate action and seek fresh air if you suspect carbon monoxide poisoning and to seek medical attention promptly.
Approach Solution -2
Question can also be asked as
- What is the mechanism behind carbon monoxide poisoning?
- What are the measures taken to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning?
- What is carbon monoxide poisoning?
- Write the symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Approach Solution -3
Carbon monoxide is a colourless and odourless gas. It is produced by the incomplete combustion of coal, wood etc. CO will bind to hemoglobin thus reducing the oxygen content that is transported. CO is fatal and is a significant public concern.
Causes of Carbon monoxide
CO can be produced in the atmosphere by the following ways:
- Automobile exhaust
- Heating system
- Cooking equipment
- Tobacco smoke
- Fireplaces and wood stoves

Symptoms of Carbon monoxide poisoning
Some of the common symptoms of CO poisoning are as follows:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weakness and fatigue
- Headaches
- Chest pains
- Loss of consciousness
- Disorientation
Prevention of CO poisoning
CO poisoning can be prevented by the following ways:
- Car and trucks should not be left running in the garages
- In industrial areas, CO detectors should be installed.
- Fuel burning applications, should be shifted to outside to prevent the CO indoors
- Smoking should be avoided in the indoor
Read more:
Learn with videos:
Top Questions on Environmental Chemistry
- Minamata disease is caused by .......... poisoning.
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Environmental Chemistry
- Which of the following is dominantly responsible for buffering capacity of natural water?
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Atmospheric Science
- Environmental Chemistry
- Which one of the following are the commonly used oxidants in COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) assays?
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Environmental Science
- Environmental Chemistry
- The octet rule is not valid for which one of the following molecules?
- LPUNEST - 2025
- Chemistry
- Environmental Chemistry
- Polyhalogen compounds have wide application in industries and agriculture. DDT is also a very important polyhalogen compound. It is a:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Chemistry
- Environmental Chemistry
Questions Asked in MHT CET exam
- A die was thrown \( n \) times until the lowest number on the die appeared. If the mean is \( \frac{n}{g} \), then what is the value of \( n \)?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Probability
Which part of root absorb mineral?
- MHT CET - 2025
- The Root
- A body of mass 2 kg is moving in a circular path of radius 3 m with a constant speed of 6 m/s. What is the centripetal force acting on the body?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Centripetal forces
- A 200 g sample of water at 80°C is mixed with 100 g of water at 20°C. Assuming no heat loss to the surroundings, what is the final temperature of the mixture?
- MHT CET - 2025
- thermal properties of matter
- Given the equation: \[ 81 \sin^2 x + 81 \cos^2 x = 30 \] Find the value of \( x \).
- MHT CET - 2025
- Trigonometric Identities
Concepts Used:
Environmental Chemistry
Environmental chemistry is the study of chemical processes and their impacts on the natural environment. It is a multidisciplinary field that combines principles from chemistry, ecology, biology, and geology to understand the complex interactions between chemicals and living organisms.
Environmental chemists investigate how pollutants such as toxic metals, organic chemicals, and pesticides affect ecosystems, including soil, water, and air. They also develop methods to monitor and measure these pollutants, as well as techniques for their removal or remediation.
Environmental chemistry also examines the impact of natural processes on the environment, such as the cycling of nutrients and the chemical reactions that occur in the atmosphere, oceans, and soil. This research can inform policy decisions related to environmental protection and management.
Read More: Difference Between Environment and Ecology
Examples of environmental chemistry applications include studying the effects of acid rain on ecosystems, developing methods for treating contaminated water and soil, and understanding the sources and fate of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Overall, environmental chemistry plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing environmental problems, and it is essential for ensuring a sustainable future for our planet.
