Upon addition of compound ( X ) to an aqueous AgNO(_3) solution, a white precipitate appears instantly. Also, ( X ) does not exhibit geometrical isomerism. The CORRECT option(s) for ( X ) is/are:
Show Hint
- ([Cr(OH_2)_4Cl_2]Cl)
- ([Cr(OH_2)_5Cl]Cl_2)
- ([Cr(OH_2)_6]Cl_3)
- ([Cr(OH_2)_3Cl_3])
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
Step 1: Understanding the reaction with AgNO\(_3\).
When a coordination compound reacts with AgNO\(_3\) to give a white precipitate of AgCl, it indicates the presence of free chloride ions (\(\text{Cl}^-\)) in the solution. The number of such free chloride ions depends on the charge of the coordination complex.
Step 2: Analyzing the options.
- Option (A): \([\text{Cr}(\text{OH}_2)_4\text{Cl}_2]\text{Cl}\)
This compound has 1 free \(\text{Cl}^-\) ion in solution. However, it exhibits geometrical isomerism due to the cis/trans arrangement of the two chlorides within the coordination sphere, so it is incorrect.
- Option (B): \([\text{Cr}(\text{OH}_2)_5\text{Cl}]\text{Cl}_2\)
This compound has 2 free \(\text{Cl}^-\) ions in solution. Since all ligands within the coordination sphere are monodentate and symmetrical, it does not exhibit geometrical isomerism, making this option correct.
- Option (C): \([\text{Cr}(\text{OH}_2)_6]\text{Cl}_3\)
This compound has 3 free \(\text{Cl}^-\) ions in solution. It has no geometrical isomers as all ligands are identical, making this option correct.
- Option (D): \([\text{Cr}(\text{OH}_2)_3\text{Cl}_3]\)
This compound does not have any free \(\text{Cl}^-\) ions in solution, as all chlorides are within the coordination sphere. Moreover, it exhibits geometrical isomerism, making this option incorrect.
Step 3: Conclusion.
The compounds \([\text{Cr}(\text{OH}_2)_5\text{Cl}]\text{Cl}_2\) and \([\text{Cr}(\text{OH}_2)_6]\text{Cl}_3\) satisfy the conditions given in the question, making options (B) and (C) correct.
Top Questions on Optical and geometrical isomerism
- The molecules A and B are a pair of___
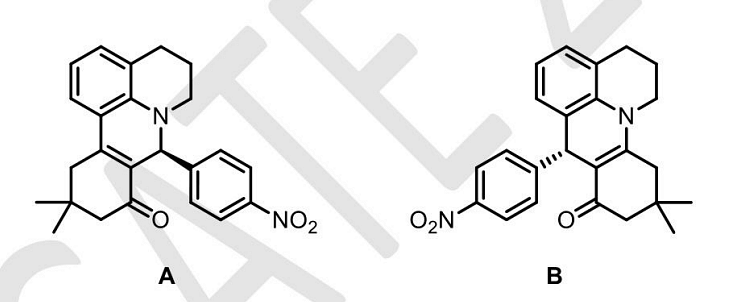
- GATE XL - 2024
- Chemistry
- Optical and geometrical isomerism
- The molecules A and B are a pair of___

- GATE XL - 2024
- Chemistry
- Optical and geometrical isomerism
- Which of the following compound does not exhibit geometrical Isomerism?
- AP EAPCET - 2023
- Chemistry
- Optical and geometrical isomerism
- Phenol is manufactured from hydrocarbon, Cumene. Cumene is chemically:
- CUET (UG) - 2023
- Chemistry
- Optical and geometrical isomerism
Questions Asked in GATE XL exam
- Which enzyme is used to join two DNA fragments in genetic engineering?
- GATE XL - 2026
- Biotechnology
- Which pyramid is always upright in an ecosystem?
- The DNA double helix is stabilized primarily by:
- The process of conversion of nitrogen into ammonia by bacteria is called:
- GATE XL - 2026
- Microbiology
- Which of the following amino acids is essential in human diet?
- GATE XL - 2026
- Biochemistry