The treatment of galena with $HNO _3$ produces a gas that is
- paramagnetic
- bent in geometry
- an acidic oxide
- colorless
The Correct Option is A, D
Solution and Explanation
The reaction of galena (PbS) with nitric acid (HNO₃) produces sulfur dioxide (SO₂) as the gas. The reaction is as follows:
\(\text{PbS} + 2\text{HNO}_3 \rightarrow \text{Pb(NO}_3)_2 + \text{SO}_2 + \text{H}_2\text{O}\)
The gas produced is sulfur dioxide (SO₂), which is a colorless gas with a pungent odor.
Now, let's analyze the properties of sulfur dioxide (SO₂), the gas produced during this reaction:
- Paramagnetic: Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) is paramagnetic because it has an unpaired electron in its molecular orbital, which causes it to be attracted by a magnetic field. SO₂ has a bent molecular geometry and contains an odd number of electrons.
- Bent in Geometry: The molecular geometry of SO₂ is bent due to the lone pairs of electrons on the sulfur atom, which causes repulsion. However, this does not directly relate to the gas properties as described in the options.
- Acidic Oxide: SO₂ is an acidic oxide because it reacts with water to form sulfurous acid (H₂SO₃). While this is true, the question primarily asks about the properties of the gas produced, which is sulfur dioxide.
- Colorless: SO₂ is colorless under standard conditions, making it a colorless gas.
Now, let's evaluate the given options:
- Option A: "Paramagnetic" – This is correct because SO₂ is paramagnetic due to its unpaired electron.
- Option B: "Bent in geometry" – This is incorrect because while SO₂ has bent geometry, the focus of the question is on the gas properties, not its molecular geometry.
- Option C: "An acidic oxide" – While SO₂ is indeed an acidic oxide, the primary focus of the question is on the gas properties (paramagnetic and colorless).
- Option D: "Colorless" – This is correct because SO₂ is a colorless gas under standard conditions.
Final Answer: The correct options are: A and D.
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
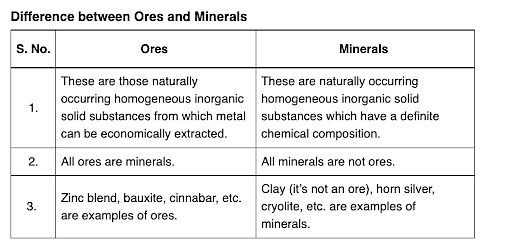
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal