The molecule which has zero dipole moment is
- $CH_3Cl$
- $NF_3$
- $BF_3$
- $ClO_2$
The Correct Option is C
Approach Solution - 1
Approach Solution -2
Dichloromethane, CH2Cl2, has two C-H bonds with dipole moments pointing in the direction of the carbon atom and two C-F bonds with dipole moments pointing outward. As a result, the dipole moments are amplifying one another, and the red arrow indicates that there is a dipole moment overall that is not zero.
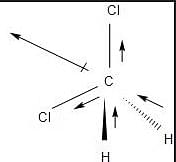

The lone pair and unsymmetrical structure of the NF3 molecules, which have a pyramidal shape, give them an overall positive dipole moment.
The two C=O bonds in the ClO2 molecule are also in opposition to one another, but the lone pair on the chlorine atom prevents the dipole from being canceled.
Top Questions on Hybridisation
Arrange the following in increasing order of solubility product:
\[ {Ca(OH)}_2, {AgBr}, {PbS}, {HgS} \]- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
Concentrated nitric acid is labelled as 75% by mass. The volume in mL of the solution which contains 30 g of nitric acid is:
Given: Density of nitric acid solution is 1.25 g/mL.- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
Match List - I with List - II.
List - I (Saccharides) List - II (Glycosidic linkages found)
(A) Sucrose (I) \( \alpha 1 - 4 \)
(B) Maltose (II) \( \alpha 1 - 4 \) and \( \alpha 1 - 6 \)
(C) Lactose (III) \( \alpha 1 - \beta 2 \)
(D) Amylopectin (IV) \( \beta 1 - 4 \)Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
Match List - I with List - II.
List - I (Complex) List - II (Hybridisation) (A) \([\text{CoF}_6]^{3-}\) (I) \( d^2 sp^3 \) (B) \([\text{NiCl}_4]^{2-}\) (II) \( sp^3 \) (C) \([\text{Co(NH}_3)_6]^{3+}\) (III) \( sp^3 d^2 \) (D) \([\text{Ni(CN}_4]^{2-}\) (IV) \( dsp^2 \)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
- The change in hybridisation (if any) of the 'Al' atom in the following reaction is
AlCl3 + Cl- → AlCl4-
- KCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
Questions Asked in JCECE exam
- In the figure, the ball P is released from rest, when the spring is at its natural length. For the block Q of mass $ 2{{m}_{0}} $ to leave contact with ground at some stage, the minimum mass of P must be
- JCECE - 2015
- Conservation of energy
- The effective resistance across the points P and Q is
- JCECE - 2015
- Current electricity
- A $ 50\,\Omega $ galvanometer is shunted by a resistance of $ 5\,\Omega . $ The percentage of the total current, which passes through the galvanometer is
- JCECE - 2015
- Current electricity
- A disc of radius a and mass m is pivoted at the rim and is set in small oscillation. If a simple pendulum have the same period as that of the disc, then the length of the simple pendulum should be
- JCECE - 2015
- Waves and Oscillations
- An elliptically shaped ring of dimensions shown in figure just touches, the horizontal surface of a liquid of surface tension S. The force required to pull the ring away from the liquid surface is
- JCECE - 2015
- Surface Tension
Concepts Used:
Hybridisation
Hybridization refers to the concept of combining atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals that are appropriate to represent their bonding properties. Hybridization influences the bond length and bond strength in organic compounds.
Types of Hybridization:
sp Hybridization
sp hybridization is observed while one s and one p orbital inside the identical principal shell of an atom mix to shape two new equal orbitals. The new orbitals formed are referred to as sp hybridized orbitals.
sp2 Hybridization
sp2 hybridization is observed whilst ones and p orbitals of the same shell of an atom blend to shape three equivalent orbitals. The new orbitals formed are referred to as sp2 hybrid orbitals.
sp3 Hybridization
When one ‘s’ orbital and 3 ‘p’ orbitals belonging to the identical shell of an atom blend together to shape 4 new equal orbitals, the sort of hybridization is referred to as a tetrahedral hybridization or sp3.
sp3d Hybridization
sp3d hybridization involves the joining of 3p orbitals and 1d orbital to form 5 sp3d hybridized orbitals of identical energy. They possess trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
sp3d2 Hybridization
With 1 s three p’s and two d’s, there is a formation of 6 new and identical sp3d2 orbitals.