The maximum temperature that can be achieved in blast furnace is
The maximum temperature that can be achieved in blast furnace is
upto 5000 K
upto 1200 K
upto 2200 K
upto 1900 K
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
To determine the correct answer, let's explore the fundamental concept of a blast furnace and its operation in the context of temperature.
A blast furnace is a crucial component in the process of extracting iron from its ores. Its primary function is to smelt iron ores to produce iron. The temperatures required in a blast furnace can vary significantly, especially since it involves chemical reactions that reduce iron oxides to iron.
The highest temperature achieved within the blast furnace occurs at the bottom, near the tuyeres where the combustion of coke with added hot air occurs. This zone is crucial for the accurate melting of iron. The range of operational temperatures in a properly-functioning blast furnace is generally between 1600 K and 1900 K.
This leads us to analyze the given options:
- upto 5000 K: This temperature is excessively high for a blast furnace and is not possible with the current technological setup and materials.
- upto 1200 K: This is not a feasible maximum temperature for the effective operation of a blast furnace, given that the iron's melting point is higher than 1200 K.
- upto 2200 K: While higher temperatures can be achieved, 2200 K exceeds regular operational parameters for standard iron production in a blast furnace.
- upto 1900 K: This aligns with the typical highest temperatures achievable within a blast furnace, fitting standard operation requirements.
Given the standard operation of a blast furnace, the best plausible choice among the options is upto 1900 K. Therefore, the initially indicated "correct" answer, upto 1200 K, appears to be incorrect, and upto 1900 K should be the correct answer based on practical knowledge of blast furnace operation.
Top Questions on Solubility Equilibria Of Sparingly Soluble Salts
- Consider three metal chlorides $x$, $y$ and $z$, where $x$ is water soluble at room temperature, $y$ is sparingly soluble in water at room temperature and $z$ is soluble in hot water. $x$, $y$ and $z$ are respectively ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Solubility Equilibria Of Sparingly Soluble Salts
The correct stability order of the following diazonium salts is:

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Solubility Equilibria Of Sparingly Soluble Salts
Arrange the following carbanions in the decreasing order of stability:
I. $p$-$\mathrm{Br{-}C_6H_4{-}CH_2^-}$
II. $\mathrm{C_6H_5{-}CH_2^-}$
III. $p$-$\mathrm{CH_3O{-}C_6H_4{-}CH_2^-}$
IV. $p$-$\mathrm{CHO{-}C_6H_4{-}CH_2^-}$
V. $p$-$\mathrm{CH_3{-}C_6H_4{-}CH_2^-}$
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Solubility Equilibria Of Sparingly Soluble Salts
- What is the pH of a solution with a \( \text{H}^+ \) concentration of \( 1 \times 10^{-3} \) mol/L?
- VITEEE - 2025
- Chemistry
- Solubility Equilibria Of Sparingly Soluble Salts
- Equal volumes of two solutions A and B of a strong acid having pH = 6.0 and pH = 4.0 respectively are mixed together to form a new solution. The pH of the new solution will be in the range:
- WBJEE - 2025
- Chemistry
- Solubility Equilibria Of Sparingly Soluble Salts
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
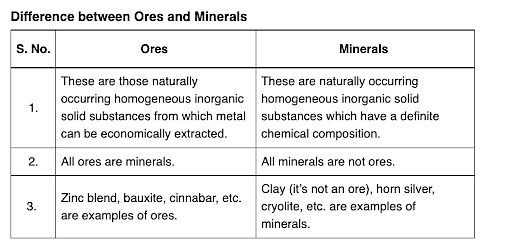
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal