The maximum area of a rectangle inscribed in the circle $(x + 1)^2 + (y - 3)^2 = 64$ is
- 64 s units
- 72 s units
- 128 s units
- 8 s units
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
The area of a rectangle inscribed in a circle is maximum, when it is a square.
$\Rightarrow(\text { diagonal })^{2}=(\text { side })^{2}+(\text { side })^{2}$
$\Rightarrow$ (diameter) $^{2}=2$ (side) $^{2}$
(because diagonal = diameter)
$\Rightarrow \frac{(16)^{2}}{2}=(\text { side })^{2}$
$\therefore$ Area $=128$ s units
Top Questions on Approximations
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives
Concepts Used:
Approximations
The theory that is part of mathematics is the approximation theory. An approximation is employed when it becomes difficult to seek out the exact value of any number. It is also essential to round off the errors resulting in approximation.
Symbol of Approximation:
In general, the wavy equal “≈” sign is used to represent the approximate values that stand for “almost equal to”.
For Example ⇢ π ≈ 3.14
Approximations of Derivatives:
Consider y = f(x) = any function of x.
Let,
Δx = the small change in x
Δy = the corresponding change in y
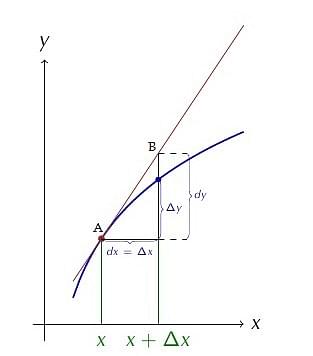
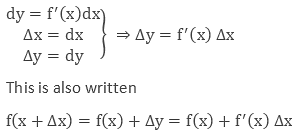
Here are some of the essential points that are required to be remembered:
- The differential of the dependent variable can not be equal to the increase of the variable whereas the differential of the independent variable can be equal to the increase of the variable.
- Absolute error in x is the change Δx.