The major product formed in the following reaction is
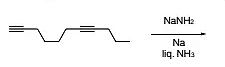
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
The Birch reduction is a process in which alkynes react with alkali metals (such as sodium, Na) in liquid ammonia (NH3) to produce trans-alkenes.
This reduction specifically targets internal alkynes, causing them to form trans-alkenes. Terminal alkynes, however, do not undergo this reduction and remain unaffected by the reaction.
Step 2: The Reaction Mechanism
When an alkyne undergoes Birch reduction, the alkali metal (sodium) donates electrons to the alkyne, resulting in the formation of a radical anion. This species reacts with ammonia to form a trans-alkene.
This reduction is selective and works primarily for internal alkynes, converting them to trans-alkenes. Terminal alkynes do not participate in this reaction and remain unchanged.
Step 3: Key Feature of the Reaction
The key characteristic of Birch reduction is the formation of **trans-alkenes** from internal alkynes. This transformation does not occur with terminal alkynes, making them unreactive under these conditions.
Step 4: Conclusion
Option (B) correctly describes this characteristic behavior of alkynes under Birch reduction conditions. It specifies that alkynes undergo Birch reduction in liquid ammonia to form trans-alkenes, while terminal alkynes do not undergo this reduction.

It is a case of Birch reduction. Alkynes on reaction with alkali metal in liq. NH3 gives trans-alkene. But terminal alkynes do not get reduced.
The correct answer is option (B):
Approach Solution -2

Option (B) states that alkynes undergo Birch reduction in liquid ammonia to form trans-alkenes, but terminal alkynes do not undergo this reduction. This succinctly summarizes the process known as Birch reduction, where alkynes react with alkali metals in liquid ammonia to produce trans-alkenes, except for terminal alkynes, which remain unaffected by this reaction. Therefore, option (B) accurately describes the characteristic behavior of alkynes under Birch reduction conditions.
Top Questions on introduction to organic chemistry
- Which of the following represents the correct IUPAC name for \( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{OH} \)?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Chemistry
- introduction to organic chemistry
- Which of the following represents the correct IUPAC name for \( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{OH} \)?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Chemistry
- introduction to organic chemistry
- What is the IUPAC name of CH$_3$CH(OH)CH$_3$?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Chemistry
- introduction to organic chemistry
- What is the concentration of \( \text{H}^+ \) ions if the pH is 2.7?
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- introduction to organic chemistry
- Calculate the pH of the solution using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
- MHT CET - 2024
- Chemistry
- introduction to organic chemistry
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that involves the scientific study of organic compounds. Organic chemistry primarily deals with the structure and chemical composition of organic compounds, the physical and chemical properties of organic compounds, and the chemical reactions undergone by these compounds.
Reaction Intermediates in Organic Chemistry:
Intermediates can be understood as the first product of a consecutive reaction. For example, in a chemical reaction, if A→B and B→C, then, B can be said to be the intermediate for reaction A→C. The reactions in organic chemistry occur via the formation of these intermediates.
Reagents in Organic Chemistry:
Reagents are the chemicals that we add to bring about a specific change to an organic molecule. Any general reaction in organic chemistry can be written as:
Substrate + Reagent → Product
Where the substrate is an organic molecule to which we add the reagent. Based on the ability to either donate or abstract electrons, the reagents can be classified as:
- Electrophiles
- Nucleophiles


