The lungs are covered by _____ membrane.
- pleural
- pericardial
- meninges
- vitelline
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on The respiratory system
- Which of the following interventions facilitates the removal of airway secretions collected centrally?
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- MPT
- The respiratory system
- Which of the following is a non-modifiable risk factor for the development of COPD?
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- MPT
- The respiratory system
- Arrange the following in the correct sequence of branching in conducting zone and respiratory zone of respiratory passage.
(A) Alveolar sacs
(B) Bronchi
(C) Bronchioles
(D) Trachea
(E) Alveolar ducts
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- MPT
- The respiratory system
- The TCA cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl group with
- KCET - 2025
- Biology
- The respiratory system
- Which of the following is the primary site of gaseous exchange in the human respiratory system?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- The respiratory system
Questions Asked in COMEDK UGET exam
- Given that the freezing point of benzene is $ 5.48^\circ C $ and its $ K_f $ value is $ 5.12^\circ C/m $, what would be the freezing point of a solution of 20 g of propane in 400 g of benzene?
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Colligative Properties
200 ml of an aqueous solution contains 3.6 g of Glucose and 1.2 g of Urea maintained at a temperature equal to 27$^{\circ}$C. What is the Osmotic pressure of the solution in atmosphere units?
Given Data R = 0.082 L atm K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$
Molecular Formula: Glucose = C$_6$H$_{12}$O$_6$, Urea = NH$_2$CONH$_2$- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Colligative Properties
- An inorganic compound W undergoes the following reactions: $ W + \text{Na}_2\text{CO}_3 \xrightarrow{\text{O}_2 / \text{heat}} X + H^+ \xrightarrow{} Y(s) $ $ Y(aq) + \text{KCl} (aq) \xrightarrow{} Z(s) $ Z appears in the form of orange crystals and is used as an oxidising agent in acid medium. Identify the compound W.
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- coordination compounds
- A current of 3.0 A is passed through 750 ml of 0.45 M solution of CuSO₄ for 2 hours with a current efficiency of 90\%. If the volume of the solution is assumed to remain constant, what would be the final molarity of CuSO₄ solution?
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Solutions
- For a reaction $ 5X + Y \to 3Z $, the rate of formation of Z is $ 2.4 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{mol L}^{-1} \text{s}^{-1} $. Calculate the average rate of disappearance of X.
- COMEDK UGET - 2024
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
Concepts Used:
The Respiratory System
Human Respiratory System is a compound biological system of organs and tissues that helps in gaseous exchange. The system includes airways, lungs, and blood vessels. Its core function is to introduce oxygen and expel carbon dioxide from the body. The atmospheric air is continuously pumped in and out through a system of pipes which are called the conducting airways. There are a great number of muscles and blood vessels involved in the whole process of respiration.
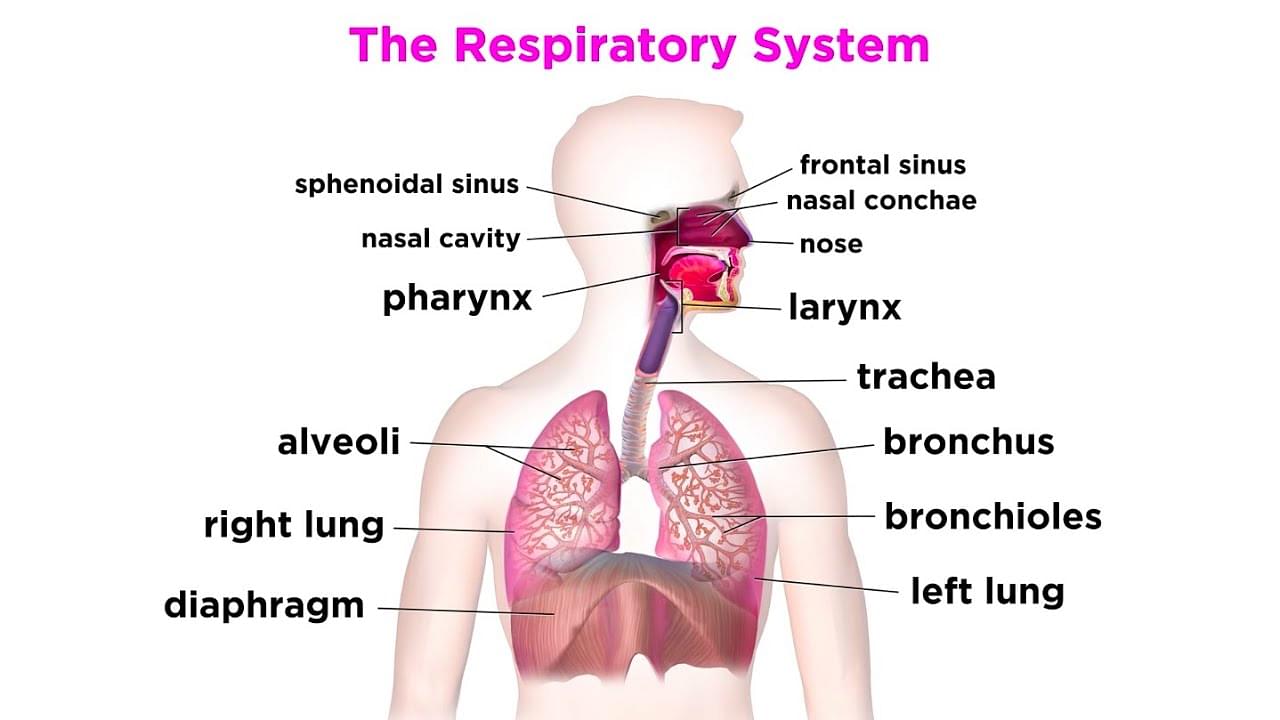
Features of Human Respiratory System:
- The respiratory system is essential for inhalation of oxygen and transportation of the same to the different parts of the body where it is used for cellular respiration.
- The design of the lungs is created in a manner that helps in gaseous exchange in an efficient manner. The other parts of the respiratory system such as the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi help in the process of bringing in oxygen to the lungs and taking carbon dioxide out of it.
- There is an arrangement of muscles such as the diaphragm and intercostal muscles that aid in the process of human respiration.