Question:
The compressibility factor $(Z)$ of one mole of a van der Waals gas of negligible $�a�$ value is
The compressibility factor $(Z)$ of one mole of a van der Waals gas of negligible $�a�$ value is
Updated On: Jul 28, 2024
- $1$
- $\frac{bp}{RT}$
- $1+\frac{bp}{RT}$
- $1-\frac{bp}{RT}$
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
van der Waals' equation is
$\left(p+\frac{a}{V^{2}}\right)(V-b)=R T\,\,\,$(for 1 mole)
If $a$ is negligible, $p+\frac{a}{V^{2}} \approx p$
$p(V-b)=R T $
$\Rightarrow p V-p b=R T $
or $\frac{p V}{R T}-\frac{p b}{R T}=1 $
$\Rightarrow \frac{p V}{R T}=1+\frac{p b}{R T}$
$\left(p+\frac{a}{V^{2}}\right)(V-b)=R T\,\,\,$(for 1 mole)
If $a$ is negligible, $p+\frac{a}{V^{2}} \approx p$
$p(V-b)=R T $
$\Rightarrow p V-p b=R T $
or $\frac{p V}{R T}-\frac{p b}{R T}=1 $
$\Rightarrow \frac{p V}{R T}=1+\frac{p b}{R T}$
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Van Der Waals equation
- Molar volume ($ V_m $) of a van der Waals gas can be calculated by expressing the van der Waals equation as a cubic equation with $ V_m $ as the variable. The ratio (in mol dm$^{-3}$) of the coefficient of $ V_m^2 $ to the coefficient of $ V_m $ for a gas having van der Waals constants $ a = 6.0 \, \text{dm}^6 \, \text{atm mol}^{-2} $ and $ b = 0.060 \, \text{dm}^3 \, \text{mol}^{-1} $ at 300 K and 300 atm is ____. Use: Universal gas constant $ R = 0.082 \, \text{dm}^3 \, \text{atm mol}^{-1} \, \text{K}^{-1} $
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- Arrange the following gases in increasing order of van der Waals constant 'a'
A. Ar
B. CH4
C. H₂O
D. C6H6
Choose the correct option from the following.- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- Which of the following statemnt is incorect for physisorption?
- GUJCET - 2023
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- At low pressure, the van der Waal's equation is reduced to
- VITEEE - 2019
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- If $V$ is the volume of one molecule of gas under given conditions, the van der Waal?s constant $b$ is
- BITSAT - 2018
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
View More Questions
Questions Asked in WBJEE exam
- Figure shows the graph of angle of deviation \( \delta \) versus angle of incidence \( i \) for a light ray striking a prism. The prism angle is

- WBJEE - 2025
- Refraction Through A Prism
- Ruma reached the metro station and found that the escalator was not working. She walked up the stationary escalator with velocity \( v_1 \) in time \( t_1 \). On another day, if she remains stationary on the escalator moving with velocity \( v_2 \), the escalator takes her up in time \( t_2 \). The time taken by her to walk up with velocity \( v_1 \) on the moving escalator will be:
- WBJEE - 2025
- Relative Motion
- The compound(s) showing optical activity is/are
- WBJEE - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about the given compound?

- WBJEE - 2025
- Organic Chemistry
- X is an extensive property and x is an intensive property of a thermodynamic system. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
- WBJEE - 2025
- Thermodynamics
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Van Der Waals Equation
Van der Waals equation is an equation relating the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of real gases.
Read More: Derivation of Van Der Waals Equation
Derivation of Van der Waals equation:
For a real gas containing ‘n’ moles, the equation is written as
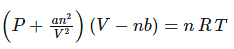
Where, P, V, T, n are the pressure, volume, temperature and moles of the gas. ‘a’ and ‘b’ constants specific to each gas.
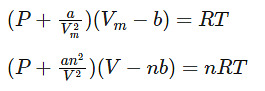
Where,
Vm: molar volume of the gas
R: universal gas constant
T: temperature
P: pressure
V: volume
Thus, Van der Waals equation can be reduced to ideal gas law as PVm = RT.
The equation can further be written as;
- Cube power of volume:
- Reduced equation (Law of corresponding states) in terms of critical constants:
Units of Van der Waals equation Constants
a: atm lit² mol-²
b: litre mol-¹