One of the 2000 years old viableseed,discovered during the archeological excavation an King Herold’s near dead sea.
- Lupin
- Sunflower
- Phoenix dactylifera
- Maize
The Correct Option is C
Approach Solution - 1
During archaeological excavations near the Dead Sea, seeds of Phoenix dactylifera, the species of palm tree that produces dates, were discovered. Some of these seeds were reported to be around 2000 years old and still viable, meaning they had the potential to germinate and grow into new plants. This discovery was significant as it provided insights into the longevity and resilience of seeds, as well as the ancient agricultural practices in the region. Therefore, the correct answer is (C) Phoenix dactylifera (date palm).
Approach Solution -2
The correct answer is:
Option 3: Phoenix dactylifera
Explanation:
The viable seed discovered during the archaeological excavation near King Herod's palace, near the Dead Sea, was of the plant Phoenix dactylifera, commonly known as the date palm. The seed, which was over 2000 years old, was successfully germinated, making it one of the oldest seeds to ever sprout.
Phoenix dactylifera (date palm) is known for its historical and cultural significance in the Middle East.
The other options are incorrect because:
Lupin (Option 1) and sunflower (Option 2) are not the seeds found in this excavation.
Maize (Option 4) is a relatively new crop compared to date palms, and it was not found in this context.
Thus, the seed discovered in the excavation near the Dead Sea was from Phoenix dactylifera.
Top Questions on The Seed
- In the seeds of cereals, the outer covering of endosperm separates the embryo by a protein-rich layer called:
- Match the content of List I with List II:Choose the correct option from the following :
List-I List-II 1 Polyembryony p Black pepper 2 Perisperm q Banana 3 False fruit r Lemon 4 Parthenocarpy s Apple - KCET - 2024
- Biology
- The Seed
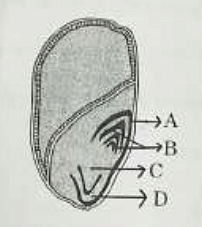
Identify the part of the seed from the given figure which is destined to form root when the seed germinates.
- What is the ideal seed rate for okra for rainy season crop?
- Which of the following is true for essentiality of germination? (A) Viability of seed
(B) Proper environment
(C) Seed free from dormancy
(D) Thin seed coat
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives