Mole fraction of the solute in a $1.00$ molal aqueous solution is
Show Hint
Mole fraction of a solute represents the ratio of the moles of the solute to the total moles of all components in the solution.
- 0.177
- 0.0177
- 0.0344
- 1.77
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
\(1.00\) molal solution means 1 mole of solute in \(1\, kg\) of water.
Number of moles of solute \(=1\)
Number of moles of solvent \(=\frac{1000}{18}=55.55\)
Mole fraction of Solute \(=\frac{1}{1+55.55}\)= 0.01768
Therefore, the correct answer is Option B)
Discover More From Chapter: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Approach Solution -2
The Correct Answer is (B)
Real Life Applications
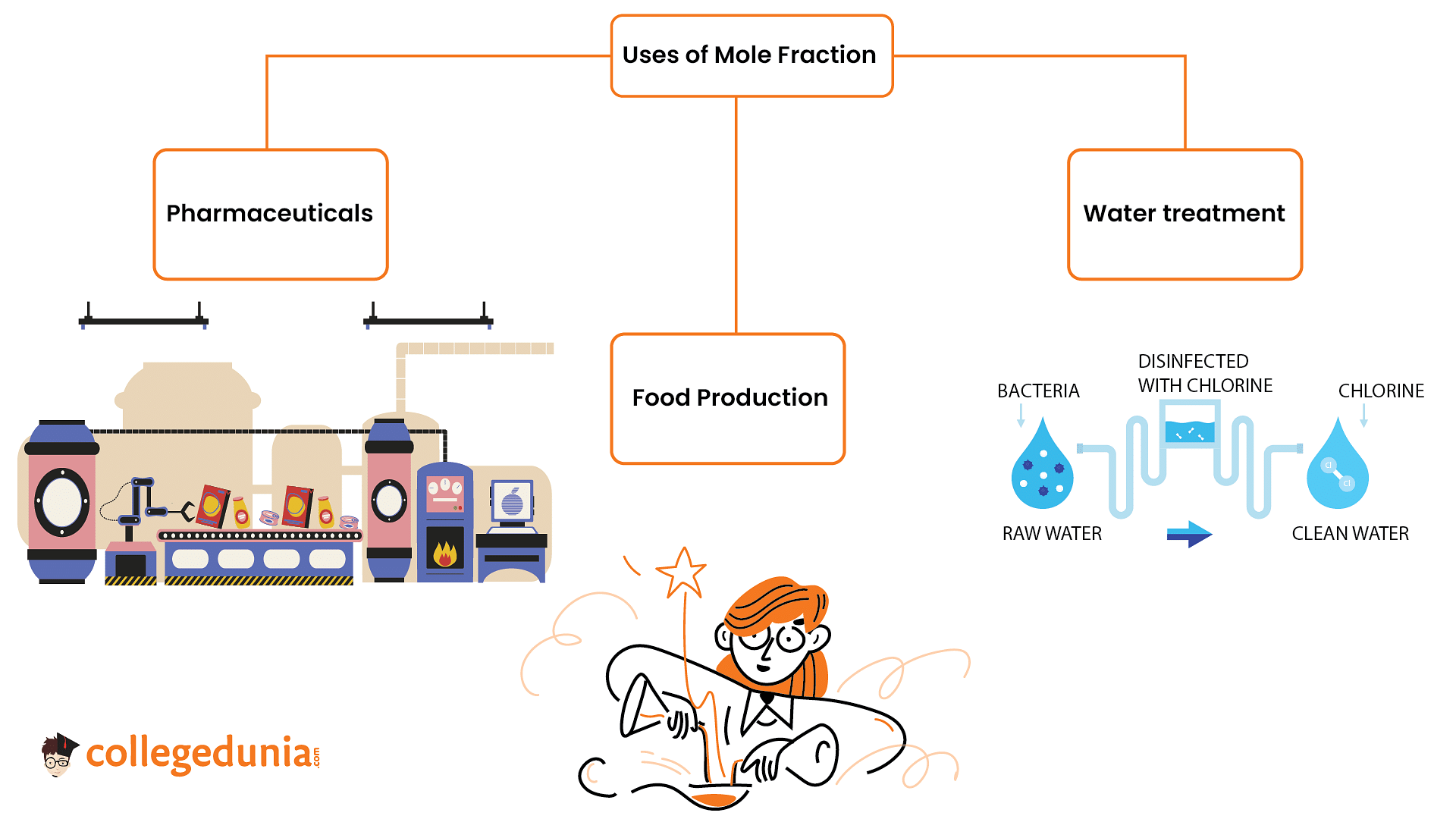
The mole fraction of the solute in a 1.00 molal aqueous solution finds practical applications in various industries:
1. Pharmaceuticals: It determines the concentration of active ingredients, ensuring accurate medication dosage.
2. Food and Beverage Industry: Controls taste and texture; for instance, the mole fraction of sugar affects sweetness in soft drinks.
3. Water Treatment: It determines the effectiveness of treatments, like the mole fraction of chlorine in killing bacteria.
4. Mole fraction helps to create solutions for specific purposes in pharmaceuticals, food production, and water treatment, contributing to product quality and safety.
Question can also be asked as
1. What is the mole fraction of the solute in a 1.00 molal aqueous solution?
2. What is the concentration of the solute in a 1.00 molal aqueous solution?
3. How much of the solute is present in a 1.00 molal aqueous solution?
4. What is the relationship between molality and mole fraction?
Approach Solution -3
The Correct Answer is (B)
In solutions, the mole fraction of a solute is a valuable parameter that represents the ratio of the moles of the solute to the total moles of all components in the solution.
Mole Fraction
- Mole fraction is a dimensionless quantity that expresses the relative amount of a component in a solution.
- It is calculated by dividing the moles of a particular component by the total moles of all components present.
Aqueous Solutions
- Aqueous solutions are solutions in which water serves as the solvent.
- These solutions often involve the dissolution of solutes, such as salts or other compounds, in water.
Molality
- Molality (molal concentration) is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution.
- It is defined as the moles of solute divided by the mass of the solvent (usually expressed in kilograms).
Calculation of Mole Fraction
- The mole fraction can be calculated by dividing the moles of the solute by the total moles of the solute and solvent.
In a 1.00 molal aqueous solution, the mole fraction of the solute is determined to be 0.0177. Mole fraction is a crucial parameter for understanding the concentration of components in a solution and plays a significant role in various applications, including colligative properties and chemical reactions.
Check Out:
Learn with videos:
Top Questions on Mole concept and Molar Masses
- 80 mL of a hydrocarbon on mixing with 264 mL of oxygen in a closed U-tube undergoes complete combustion. The residual gases after cooling to 273 K occupy 224 mL. When the system is treated with KOH solution, the volume decreases to 64 mL. The formula of the hydrocarbon is:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
- The following solutions were prepared by dissolving 1 g of solute in 1 L of the solution. Arrange the following solutions in decreasing order of their molarity: (A) Glucose (molar mass = 180 g mol$^{-1}$)
(B) NaOH (molar mass = 40 g mol$^{-1}$)
(C) NaCl (molar mass = 58.5 g mol$^{-1}$)
(D) KCl (molar mass = 7(4)5 g mol$^{-1}$)
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
- Calculate the mass in kg of 4.48 dm$^3$ carbon dioxide at STP.
- MHT CET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
- The carbohydrate used as a storage molecule in plants is
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
- Match List-I with List-II \[ \begin{array}{|l|l|l|} \hline \textbf{List-I} & \textbf{List-II} & \textbf{Matches} \\ \hline (A) \; \text{Cell constant} & (I) \; \text{cm}^{-1} & (A) - (I) \\ \hline (B) \; \text{Molar conductance} & (II) \; \Omega^{-1}\,\text{cm}^2\,\text{mol}^{-1} & (B) - (II) \\ \hline (C) \; \text{Specific conductance} & (III) \; \Omega^{-1}\,\text{cm}^{-1} & (C) - (III) \\ \hline (D) \; \text{Conductance} & (IV) \; \Omega^{-1} & (D) - (IV) \\ \hline \end{array} \]
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
Questions Asked in BITSAT exam
- What is the dot product of the vectors \( \mathbf{a} = (2, 3, 1) \) and \( \mathbf{b} = (1, -1, 4) \)?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Vector Algebra
- Find the determinant of the matrix \( A = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 \end{bmatrix} \).
- BITSAT - 2025
- Matrices
- A convex lens has focal length 20 cm. An object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the lens. What is the position of the image formed?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- What is the value of \( \sin 30^\circ \)?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Trigonometry
- The area enclosed between the curve \(y = \log_e(x + e)\) and the coordinate axes is:
- BITSAT - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Concepts Used:
Mole Concept
In the field of chemistry, a mole is defined as the amount of a substance that contains exactly 6.02214076 * 1023 ‘elementary entities’ of the given substance.
The number 6.02214076*1023 is popularly known as the Avogadro constant and is often denoted by the symbol ‘NA’. The elementary entities that can be represented in moles can be atoms, molecules, monoatomic/polyatomic ions, and other particles (such as electrons).
For example, one mole of a pure carbon-12 (12C) sample will have a mass of exactly 12 grams and will contain 6.02214076*1023 (NA) number of 12C atoms. The number of moles of a substance in a given pure sample can be represented by the following formula:
n = N/NA
Where n is the number of moles of the substance (or elementary entity), N is the total number of elementary entities in the sample, and NA is the Avogadro constant.
The word “mole” was introduced around the year 1896 by the German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald, who derived the term from the Latin word moles meaning a ‘heap’ or ‘pile.
The mole concept refers to the atomic mass of a mole that is measured in grams. The gram atomic mass of an element is known as a mole. The mole concept combines the mass of a single atom or molecule in a.m.u. to the mass of a large group of comparable molecules in grams. Atomic mass is the mass of a single atom, whereas molecular mass is the mass of a group of atoms.
The Formula of Mole Concept
The number of units that make up a mole has been calculated to be 6.022 ×10²³. The fundamental constant is also known as Avogadro's number (NA) or Avogadro constant. This constant is appropriately represented in chemistry using an explicit unit termed per mole.
Number of Moles = (Mass of the Sample)/(Molar Mass)
Read More: Mole Fraction
