Match List I with List II
LIST I Water moisture content
LIST II Defined as / Term A Gravitational water I Portion of water readily absorbed by plant roots B Capillary water II Water that moves into, through II. and and out of the soil under influence of gravity C Hygroscopic water III Water that fills the micropores of the soil D Available water IV Water held most tightly to soil particles (31 bars of suction)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match List I with List II
LIST I Water moisture content | LIST II Defined as / Term | ||
| A | Gravitational water | I | Portion of water readily absorbed by plant roots |
| B | Capillary water | II | Water that moves into, through II. and and out of the soil under influence of gravity |
| C | Hygroscopic water | III | Water that fills the micropores of the soil |
| D | Available water | IV | Water held most tightly to soil particles (31 bars of suction) |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
- A-II. B-IV, C-III, D-I
- A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
- A-I. B-II, C-III, D-IV
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on Transport of water and minerals in plants
- Match the following concerning essential elements and their functions in plants:
a Iron i Photolysis of water b Zinc ii Pollen germination c Boron iii Required for chlorophyll biosynthesis d Manganese iv IAA biosynthesis - NEET (UG) - 2020
- Biology
- Transport of water and minerals in plants
- Thiobacillus is a group of bacteria helpful in carrying out:
- NEET (UG) - 2019
- Biology
- Transport of water and minerals in plants
- The adsorption of water by hydrophilic compounds like cellulose and pectin in root hair cell wall is called _______.
- MHT CET - 2018
- Biology
- Transport of water and minerals in plants
- The lowest water potential in the xylem will be of:
- UPSEE - 2018
- Biology
- Transport of water and minerals in plants
- The water potential of pure water is :
- NEET (UG) - 2017
- Biology
- Transport of water and minerals in plants
Questions Asked in CUET PG exam
- Upper palaeolithic culture in India is dominated by:
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Which of the following species are included among gracile australopithecines?
A. A. africanus
B. A. boisei
C. A. afarensis
D. A. anamensis
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Paleoanthropology
- A bought an article at a certain price and sold it at 10% profit. B bought the same article at a price 10% lesser than A and sold it at ₹18 lesser than A. B's gain percentage in this deal is 20%. At what price B bought the article?
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Profit and Loss
- The traffic lights at three different road crossings change after every 48 seconds, 72 seconds and 108 seconds respectively. If they all change simultaneously at 8:20:00 hours, then at what time will they again change simultaneously?
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Quantitative Aptitude
- In terracotta which materials are mainly used to build strong clay
(A) Grog
(B) Metal
(C) Cotton
(D) Stone
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Ceramics and Pottery
Concepts Used:
Types of Differential Equations
There are various types of Differential Equation, such as:
Ordinary Differential Equations:
Ordinary Differential Equations is an equation that indicates the relation of having one independent variable x, and one dependent variable y, along with some of its other derivatives.
\(F(\frac{dy}{dt},y,t) = 0\)
Partial Differential Equations:
A partial differential equation is a type, in which the equation carries many unknown variables with their partial derivatives.
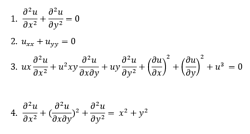
Linear Differential Equations:
It is the linear polynomial equation in which derivatives of different variables exist. Linear Partial Differential Equation derivatives are partial and function is dependent on the variable.
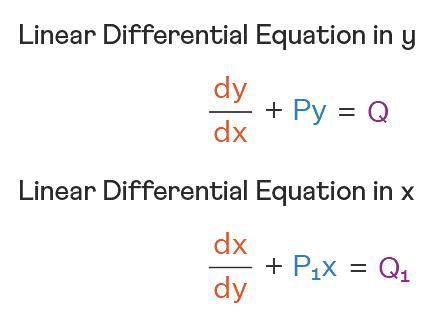
Homogeneous Differential Equations:
When the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,y) is the same, it is known to be a homogeneous differential equation.
\(\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{a_1x + b_1y + c_1}{a_2x + b_2y + c_2}\)
Read More: Differential Equations