Match items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code:


- (a) $\to$ (ii) ,(b) $\to$ (iii) ,(c) $\to$ (i) ,(d) $\to$ (v)
- (a) $\to$ (i) ,(b) $\to$ (ii) ,(c) $\to$ (iii) ,(d) $\to$ (iv)
- (a) $\to$ (iii) ,(b) $\to$ (iv) ,(c) $\to$ (v) ,(d) $\to$ (i)
- (a) $\to$ (iv) ,(b) $\to$ (ii) ,(c) $\to$ (iii) ,(d) $\to$ (i)
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
Extraction Processes
Cyanide Process:
The cyanide process is used to extract gold (Au) from its ores. The process involves the following reactions:
\(4Au + 8NaCN + O_2 + 2H_2O \to 4Na[Au(CN)_2] + 4NaOH\)
After this, the impure gold cyanide complex is treated with zinc to reduce the gold:
\(2Na[Au(CN)_2] \xrightarrow{[Zn]} \underset{\text{ppt}}{2 Au} + Na_2[Zn(CN)_4]\)
Froth Floatation Process:
The froth flotation process is used for concentrating sulphide ores. This method involves using air bubbles to separate the desired minerals from the rest of the ore by creating froth, where the mineral particles attach to the bubbles.
Electrolytic Reduction (Hall-Heroult Process):
The Hall-Heroult process is used to extract aluminium from its ore, bauxite. This process involves the electrolytic reduction of bauxite in the presence of cryolite:
Electrolytic reduction of bauxite is done by dissolving the ore in molten cryolite (Na₃AlF₆) and applying a direct current. This reduces aluminium oxide to aluminium metal at the cathode.
Zone Refining:
Zone refining is a method of purifying semiconductor materials like Germanium (Ge) and Silicon (Si). In this method, a molten zone is passed along the material, selectively dissolving impurities into the molten region, which is then moved to the next region for further purification.
Approach Solution -2
- Cyanide process: This process is used for the extraction of gold (Au), hence it is matched with (iv) Extraction of Au.
- Froth flotation process: This is used for concentrating sulphide ores like ZnS (zinc sulfide), so it is matched with (ii) Dressing of ZnS.
- Electrolytic reduction: This is the method used to extract aluminum (Al) from bauxite, so it is matched with (iii) Extraction of Al.
- Zone refining: This technique is used for purifying materials like germanium (Ge), so it is matched with (i) Ultrapure Ge.
Correct Code:
(a) → (iv), (b) → (ii), (c) → (iii), (d) → (i)
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
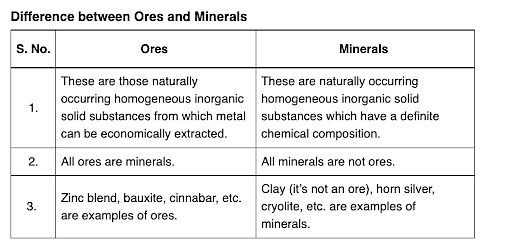
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal