In the stomach, gastric acid is secreted by the :
- Parietal cells
- Peptic cells
- Acidic cells
- Gastrin secreting cells
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
The stomach's production of hydrochloric acid is controlled by parietal cells. The pH of the stomach is brought down to 1.5 to 2.5 by gastric acid.
In the presence of an acidic pH, this secretion is critical for the function of stomach enzymes.
Additionally, it is crucial for eliminating any pathogens that may be present in the food.
In the stomach mucosa, there are many tiny tubular glands. The epithelium of the gastric glands contains parietal cells, which are more prevalent on the side walls of the glands. They are also known as oxyntic cells because eosin causes them to stain so dramatically. They release hydrochloric acid and castle intrinsic factors, both of which are necessary for vitamin B12 absorption. In the stomach, HCl maintains a highly acidic pH of 1.5 to 2.5. This eliminates germs as well as any other potentially hazardous organisms that could be present in food.
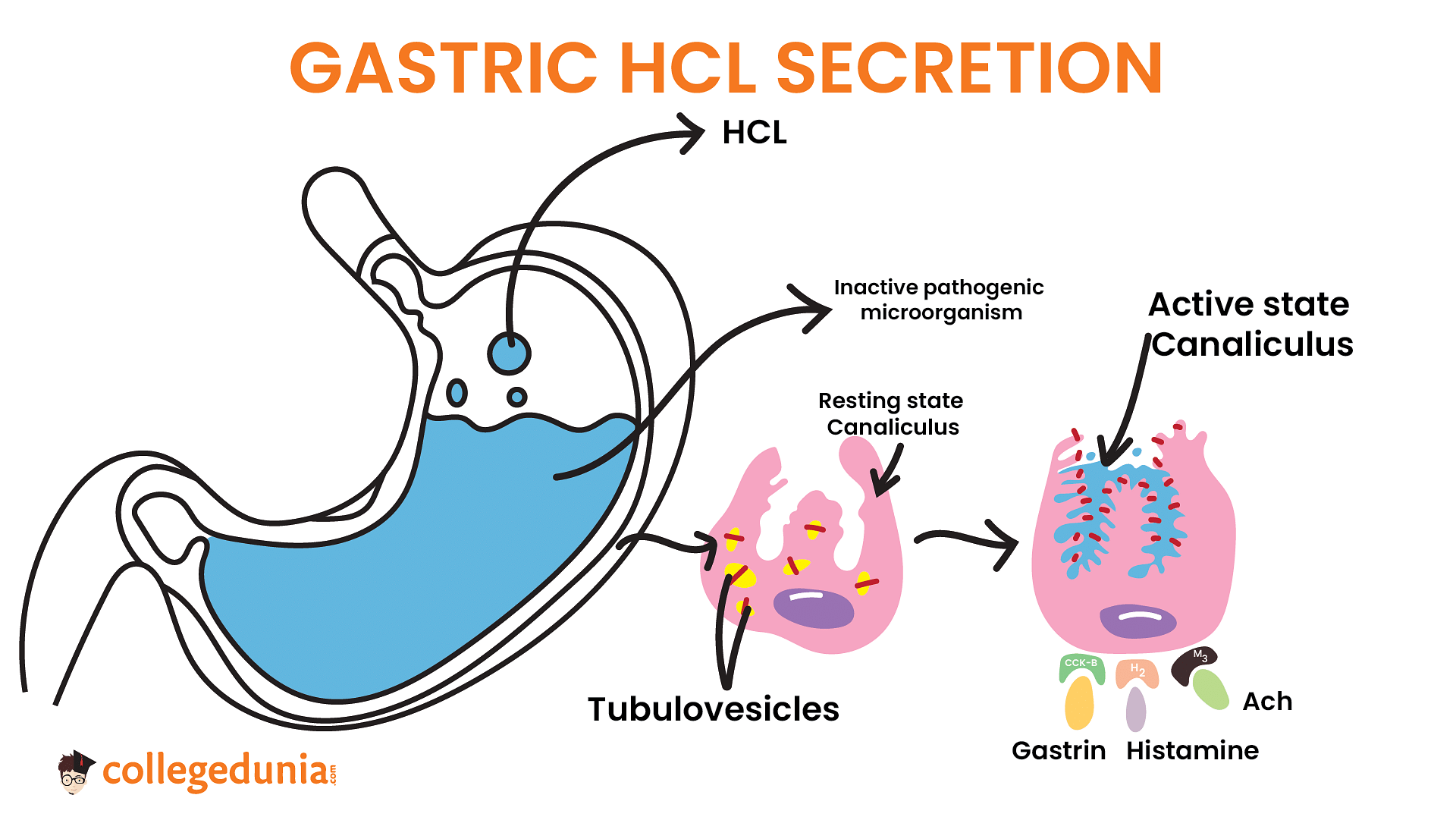
Parietal or oxyntic cells release intrinsic factors and HCl, which causes the stomach's pH to be very acidic. Pepsinogen, which is secreted by parietal glands and changed into pepsin by hydrochloric acid, is also produced. Protein is digested as a result of pepsin. Protein digestion will be directly impacted if parietal cells stop functioning.
Approach Solution -2
The correct answer is Option A) Parietal cells
Real Life Applications
- All meals, especially proteins, and many beverages increase the production of gastric acid; the most strong beverages are milk and fermented foods like beer and wine.
- Some medical procedures, including the treatment of ulcers, include the use of gastric acid.
- The acid can destroy the germs that cause ulcers and aid in destroying any scar tissue that can develop around an ulcer.
Question can also be asked as
- What cells in the stomach secrete gastric acid?
- What is the source of gastric acid in the stomach?
- Where in the stomach is gastric acid produced?
- Which cells in the stomach produce gastric acid?
- What stimulates gastric acid secretion?
- What inhibits gastric acid secretion?
- What are the functions of gastric acid?
- What are the consequences of excessive gastric acid secretion?
Approach Solution -3
The food that we eat is a complex compound that needs to be simplified. Digestion is the breakdown of complex food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed is called digestion. Human digestive system is also called the alimentary canal. It consists of all the organs and glands that are involved in the digestion of food.
Parts of stomach
Stomach is a muscular, J shaped organ that is on the left side of the upper part of the abdomen. It is the place where food gets stored for some time, there are three layers of smooth muscles:
- Outer longitudinal
- Middle circular
- Inner oblique fibres
Parts of the stomach
There are four parts: Cardiac, fundus, body and pyloric
Cardiac: It is the upper region of the stomach. The opening is called cardiac aperture and opening consists of a valve which is called the cardiac sphincter.
Fundus: It is above the cardiac part and is dome shaped.
Body: it is the middlemost part of the stomach
Pyloric: it is the lowest region of the stomach. It transfers food from the stomach to the small intestine called the pyloric canal.
Layers of the stomach
There are four different layers of stomach:
- Mucosa
- Sub mucosa
- Muscularis
- Serosa
Enzymes of stomach
The various enzyme are as follows:
- Mucus is secreted by the goblet cells. It protects the cell wall from HCl.
- HCL is the acid that is secreted by the oxyntic cell.
- Pepsinogen is the protein digesting enzyme.
Read more:
| Related Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Digestive enzyme | Connective tissue | Pituitary gland |
| Fatty liver | Digestive disorder | Gastric |
Learn with videos:
Top Questions on Digestion and absorption
- Study the following and pick up the correct statements:
I. Paneth cells of intestinal glands secrete lysozyme
II. Kupfer's cells are the hepatic macrophages
III. Intestinal lipase is called steapsin
IV. Oxidation of one gram of fats yields 4 k.cal of energy- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- Digestion and absorption
- Study the following and identify the correct statements:
I. Aminopeptidases are secreted by the pancreas
II. Enamel on teeth is secreted by ameloblasts
III. Dental formula of human milk dentition is 2102/2102
IV. Liver is the largest endocrine gland in the body of a man- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- Digestion and absorption
- Match List I with List II
List I List II A Lipase I Peptide bond B Nuclease II Ester bond C Protease III Glycosidic bond D Amylase IV Phosphodiester bond
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- Digestion and absorption
- The correct statement regarding the function of amylase is:
- BCECE Nursing - 2024
- Biology
- Digestion and absorption
- The enzyme present in the gastric juice of infants is:
- TS EAMCET - 2024
- Zoology
- Digestion and absorption
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
Digestion and Absorption - Alimentary Canal
Digestion can be defined as the process of breakdown of large, insoluble and complex food molecules into smaller ones for its absorption and circulation in the body. This process involves the usage of a variety of digestive fluids and enzymes, including saliva, mucus, bile and hydrochloric acid, among others.
Read More: Digestion and Absorption
The alimentary canal is mainly referred to as the pathway by which food enters our body and moves out through the anus after digestion. It is a tube-like structure that starts from the mouth and ends in the anus. The alimentary canal plays a primary role in human digestion and is also termed as the digestive tract.
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.