In the following reaction
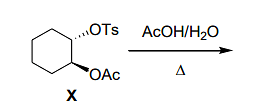
optically pure ester X formed product that did not exhibit optical rotation ([α]D=0) due to the formation of
(Note: Ts=para-toluenesulfonyl; Ac=acetyl)

optically pure ester X formed product that did not exhibit optical rotation ([α]D=0) due to the formation of
(Note: Ts=para-toluenesulfonyl; Ac=acetyl)
- cis-1,2-diacetoxycyclohexane.
- a racemic mixture of trans-1,2-diacetoxycyclohexane.
- cyclohexene.
- cyclohexene oxide.
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
In this reaction, ester X undergoes a nucleophilic substitution with acetohydroxylation, followed by rearrangement. The formation of a racemic mixture of trans-1,2-diacetoxycyclohexane occurs due to the generation of two stereoisomers (enantiomers) during the reaction. These enantiomers exhibit no optical rotation due to the racemic nature of the mixture.
Top Questions on Stereochemistry
- The heat of atomisation of methane and ethane are \( x \) kJ mol\(^{-1}\) and \( y \) kJ mol\(^{-1}\) respectively. The longest wavelength (\( \lambda \)) of light capable of breaking the C–C bond can be expressed in SI unit as:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Stereochemistry
- Heat of atomisation of CH$_4$(g) and C$_2$H$_6$(g) are $x$ kJ/mol and $y$ kJ/mol respectively. Find the maximum wavelength of photon required to dissociate C–C bond in C$_2$H$_6$.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Stereochemistry
Which of the following is true for the stereochemical relationship of the given structures (A-D)?

- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Stereochemistry
Consider the following molecule (X).
The Structure X is?

- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Stereochemistry
How many different stereoisomers are possible for the given molecule?

- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Stereochemistry
Questions Asked in IIT JAM CY exam
- Among the following, the correct condition(s) for spontaneity is(are)
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas starting from state A, goes through B and C to state D, as shown in the figure. Total change in entropy (in J K\(^{-1}\)) during this process is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- Thermodynamics
The number of chiral carbon centers in the following molecule is ...............

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
- Consider the following matrices A and B.
\[ A = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 2 & 0 & 0 \\ 3 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 5 & 5 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 6 & 7 \\ 0 & 0 & 8 & 9 \end{pmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad B = \begin{pmatrix} 10 & 11 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 12 & 13 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 4 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 15 & 16 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 17 & 18 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \]
If \( C = AB \), the sum of the diagonal elements of \( C \) is ..............
- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry
A tube fitted with a semipermeable membrane is dipped into 0.001 M NaCl solution at 300 K as shown in the figure. Assume density of the solvent and solution are the same. At equilibrium, the height of the liquid column \( h \) (in cm) is .........

- IIT JAM CY - 2025
- General Chemistry