In the context of the Hall-Heroult process for the extraction of $Al$, which of the following statements is false?
- $CO$ and $CO_2$ are produced in this process
- $Al_2O_3$ is mixed with $CaF_2$ which lowers the melting point of the mixture and brings conductivity
- $Al^{3+}$ is reduced at the cathode to form $Al$
- $Na_3AlF_6$ serves as the electrolyte
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Let \( ABC \) be a triangle. Consider four points \( p_1, p_2, p_3, p_4 \) on the side \( AB \), five points \( p_5, p_6, p_7, p_8, p_9 \) on the side \( BC \), and four points \( p_{10}, p_{11}, p_{12}, p_{13} \) on the side \( AC \). None of these points is a vertex of the triangle \( ABC \). Then the total number of pentagons that can be formed by taking all the vertices from the points \( p_1, p_2, \ldots, p_{13} \) is ___________.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Coordinate Geometry
- A voltage regulating circuit consisting of a Zener diode having breakdown voltage of $10\,\text{V}$ and maximum power dissipation of $0.4\,\text{W}$ is operated at $15\,\text{V}$. The approximate value of protective resistance in this circuit is ___ $\Omega$.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Semiconductor electronics: materials, devices and simple circuits
- Two point charges of \(1\,\text{nC}\) and \(2\,\text{nC}\) are placed at two corners of an equilateral triangle of side \(3\) cm. The work done in bringing a charge of \(3\,\text{nC}\) from infinity to the third corner of the triangle is ________ \(\mu\text{J}\). \[ \left(\frac{1}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}=9\times10^9\,\text{N m}^2\text{C}^{-2}\right) \]
- JEE Main - 2026
- Electrostatics
Consider the following two reactions A and B:

The numerical value of [molar mass of $x$ + molar mass of $y$] is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Organic Chemistry
Consider an A.P. $a_1,a_2,\ldots,a_n$; $a_1>0$. If $a_2-a_1=-\dfrac{3}{4}$, $a_n=\dfrac{1}{4}a_1$, and \[ \sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i=\frac{525}{2}, \] then $\sum_{i=1}^{17} a_i$ is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Arithmetic Progression
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
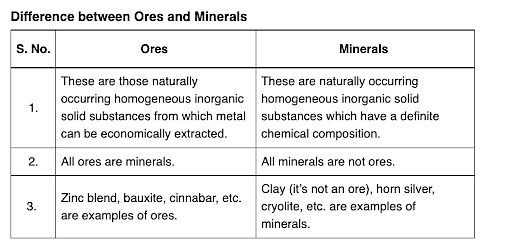
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal