If the sum of the distance of a point from two perpendicular lines in a plane is 1, then its locus is
- square
- circle
- straight line
- two intersecting lines
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
This consist of a square of side 1.
Hence, the required locus is a square.
Top Questions on Straight lines
- Rhombus vertices A(1,2), C(-3,-6). Line AD parallel to $7x-y=14$. Find $|\alpha+\beta+\gamma+\delta|$.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- Let the angles made with the positive $x$-axis by two straight lines drawn from the point $P(2,3)$ and meeting the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$ from the point $P$ be $\theta_1$ and $\theta_2$. Then the value of $(\theta_1+\theta_2)$ is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- If two lines drawn from a point $P(2,3)$ intersect the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}$, then the angle between the lines is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- If two lines drawn from a point $P(2,3)$ intersect the line $x+y=6$ at a distance $\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}$, then the angle between the lines is
- JEE Main - 2026
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
- The equation of a straight line is given by \( y = 3x + 4 \). What is the slope of the line?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Mathematics
- Straight lines
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
Straight lines
A straight line is a line having the shortest distance between two points.
A straight line can be represented as an equation in various forms, as show in the image below:
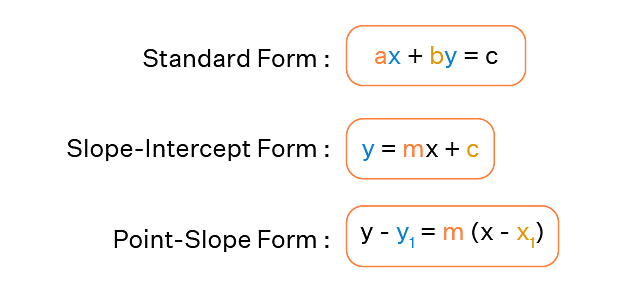
The following are the many forms of the equation of the line that are presented in straight line-
1. Slope – Point Form
Assume P0(x0, y0) is a fixed point on a non-vertical line L with m as its slope. If P (x, y) is an arbitrary point on L, then the point (x, y) lies on the line with slope m through the fixed point (x0, y0) if and only if its coordinates fulfil the equation below.
y – y0 = m (x – x0)
2. Two – Point Form
Let's look at the line. L crosses between two places. P1(x1, y1) and P2(x2, y2) are general points on L, while P (x, y) is a general point on L. As a result, the three points P1, P2, and P are collinear, and it becomes
The slope of P2P = The slope of P1P2 , i.e.
\(\frac{y-y_1}{x-x_1} = \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}\)
Hence, the equation becomes:
y - y1 =\( \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1} (x-x1)\)
3. Slope-Intercept Form
Assume that a line L with slope m intersects the y-axis at a distance c from the origin, and that the distance c is referred to as the line L's y-intercept. As a result, the coordinates of the spot on the y-axis where the line intersects are (0, c). As a result, the slope of the line L is m, and it passes through a fixed point (0, c). The equation of the line L thus obtained from the slope – point form is given by
y – c =m( x - 0 )
As a result, the point (x, y) on the line with slope m and y-intercept c lies on the line, if and only if
y = m x +c