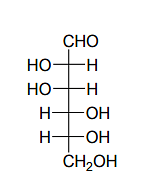
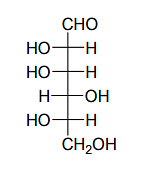
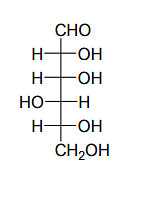
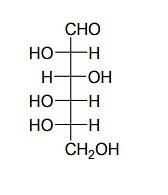Given:
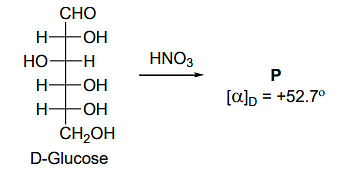
The compound(s), which on reaction with HNO3 will give the product having a degree of rotation, [α]D = –52.7º is(are);
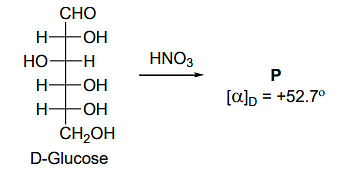
The compound(s), which on reaction with HNO3 will give the product having a degree of rotation, [α]D = –52.7º is(are);
The Correct Option is C, D
Solution and Explanation
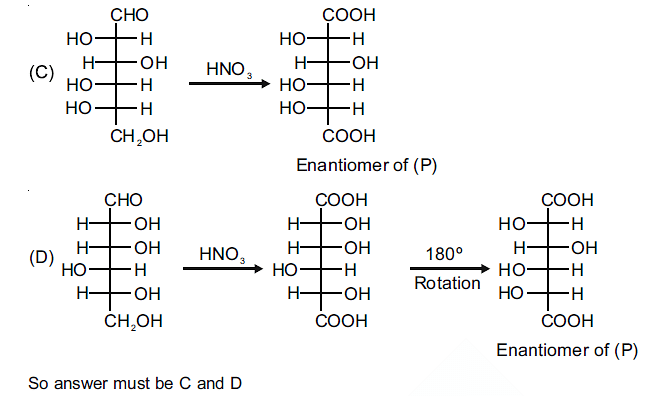
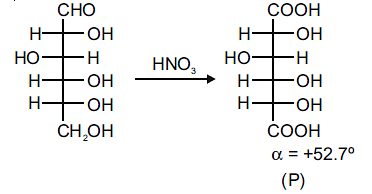 |
|
The enantiomer of (P) will have –52.7º rotation. So the reactant must be an isomer of D-glucose which can given the mirror image of (P)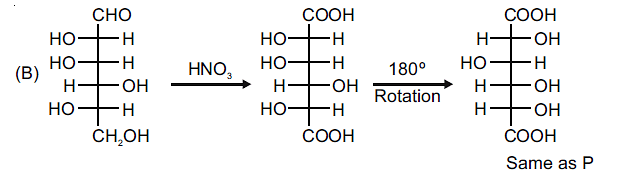
Top Questions on Glucose
Assume a living cell with 0.9% (\(w/w\)) of glucose solution (aqueous). This cell is immersed in another solution having equal mole fraction of glucose and water. (Consider the data up to first decimal place only) The cell will:
Identify correct conversion during acidic hydrolysis from the following:
(A) Starch gives galactose.
(B) Cane sugar gives equal amount of glucose and fructose.
(C) Milk sugar gives glucose and galactose.
(D) Amylopectin gives glucose and fructose.
(E) Amylose gives only glucose.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- Which of the following shows -R effect?
- Which one of the following products is NOT obtained in anaerobic decomposition of glucose ?
- Describe the development of placenta during pregnancy in a human female.
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar, also known as dextrose, that is a primary source of energy for living organisms. It is a monosaccharide, meaning it consists of a single sugar unit, and is chemically classified as an aldohexose, which means it has six carbon atoms and an aldehyde functional group.
Glucose is produced by plants through the process of photosynthesis, where it is synthesized from carbon dioxide and water using energy from sunlight. It is also produced in the human body through the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, such as starch and glycogen, in the process of digestion.
Glucose is transported throughout the body via the bloodstream and taken up by cells where it is metabolized to produce energy in the form of ATP. Excess glucose can be stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen for later use.
Read Also: Structure of Glucose and Fructose
Glucose is an important component of many foods, such as fruits, honey, and sweetened beverages. It is also used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a medical treatment for hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by low blood glucose levels.
Measurement of glucose levels in the blood is an important diagnostic tool for monitoring and managing diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels. Glucose testing can be done using a variety of methods, such as fingerstick testing and continuous glucose monitoring.